Capital preservation in trading is the discipline of protecting your principal, not chasing every return. Authoritative financial sources define the preservation of capital as prioritising loss avoidance and limiting downside risk.
For traders, that means a repeatable method for preserving capital built around drawdown control and capital-protection trading rules. This guide turns capital preservation strategies into practical actions, including a risk per trade rule, a maximum drawdown limit, and equity curve protection.
If you want the best way to preserve capital, read on and apply one rule today.

- Capital preservation in trading works best when you separate “market risk” from “process risk” and monitor both.
- Use capital preservation vs growth as a decision framework, not a goal, and switch modes when conditions change.
- A capital preservation portfolio with capital preservation asset allocation reduces operational pressure during stress, not just trading volatility.
- Capital preservation formulas are most valuable as an audit tool, because they expose hidden exposure from instrument and execution details.
What Does Capital Preservation in Trading Mean and Why Does It Matter?
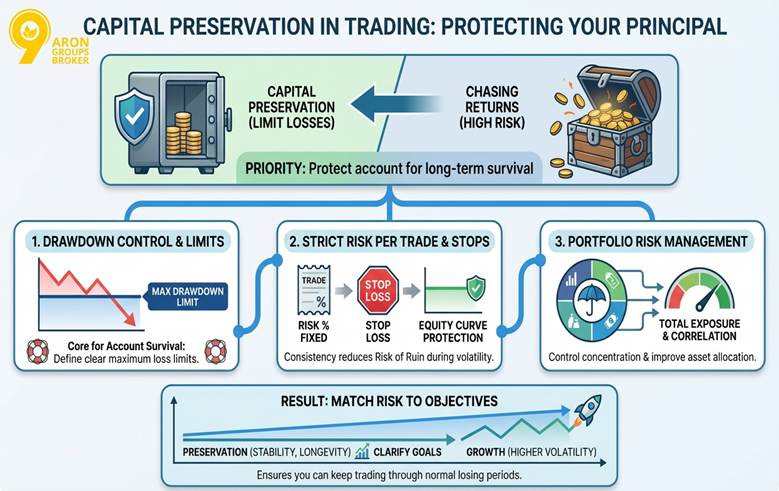
Capital preservation in trading means protecting your account so you can keep trading through normal losing periods. The preservation of capital is the priority of limiting losses and protecting principal, rather than chasing returns at any cost.
This is why drawdown control and a clear maximum drawdown limit are core to any account survival strategy.
In trading, capital preservation strategies rely on a strict risk per trade rule and consistent stop execution. This supports equity curve protection and reduces the risk of ruin when volatility rises or trades cluster negatively.
A capital preservation method also clarifies capital preservation vs growth, so you match risk to your objectives.
A capital preservation portfolio mindset means managing total exposure across positions and correlated markets. This is where determining portfolio risk helps you control concentration and improve capital preservation and asset allocation.
Q: Is capital preservation only for beginners?
A: No. According to CFI, it is a professional constraint that strengthens capital protection trading and improves long-term decision quality.
Capital Preservation vs Growth as a Practical Spectrum
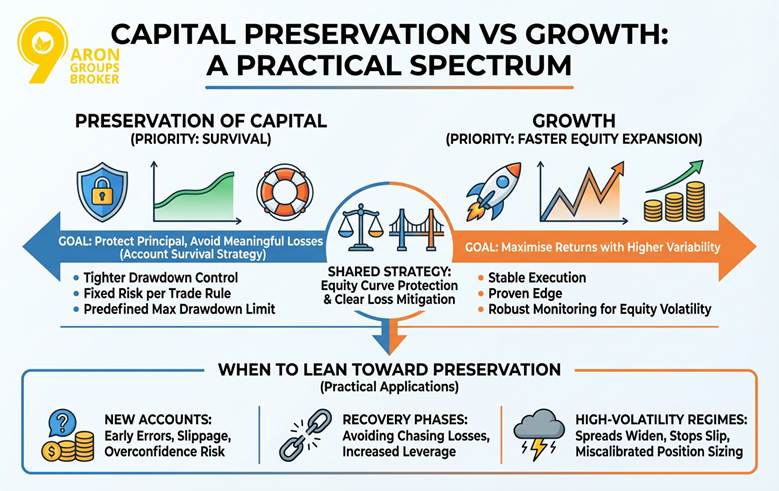
Capital preservation vs growth is best viewed as a spectrum, not a permanent identity or single trading style. In this spectrum, preservation of capital prioritises survival, while growth prioritises faster equity expansion with higher variability.
Investopedia defines capital preservation as protecting principal and avoiding meaningful losses, which fits trading risk management decisions.
Traders should prioritise capital preservation in trading when protecting the account matters more than maximising returns this month. This usually means tighter drawdown control, a fixed risk per trade rule, and a predefined maximum drawdown limit.
These limits support an account survival strategy by reducing the probability of reaching unrecoverable losses, often described as the risk of ruin.
Growth becomes more appropriate when the trader has stable execution, a proven edge, and robust monitoring for equity volatility. Even then, the best way to preserve capital is to pair growth targets with equity curve protection and a clear loss mitigation strategy.
New accounts should lean toward preservation because early errors, slippage, and overconfidence can quickly damage compounding potential.
Recovery phases also favour preservation, because chasing losses often increases leverage and breaks risk rules at the worst moment.
High-volatility regimes similarly favour preservation, because spreads widen, stops slip, and normal position sizing can become miscalibrated.

Key Insight:
Growth targets without a maximum drawdown limit can encourage destructive leverage decisions after losses, especially during recovery phases.
Core Mechanics of Capital Preservation in Trading Using Capital Protection Trading Rules
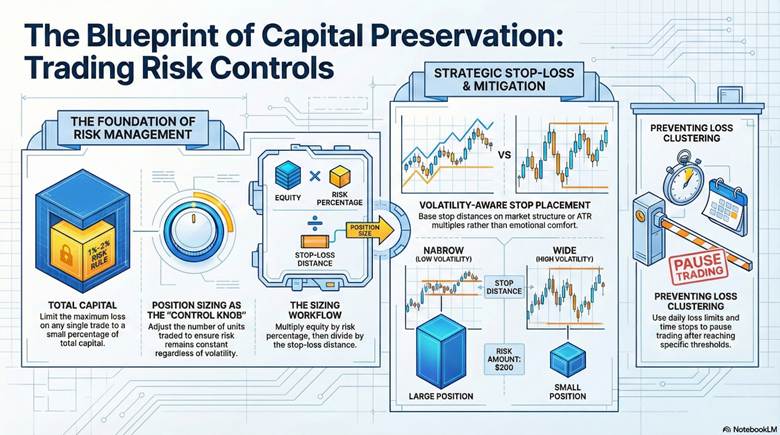
Capital preservation in trading depends less on predictions and more on enforceable risk controls. The core mechanics are position sizing, structured stop placement, and rules that prevent compounding losses.

Did You Know:
Position sizing often matters more than the entry signal, because it governs how much a mistake can cost.
Risk per Trade Rule and Position Sizing as the Capital Preservation Method
A risk per trade rule sets the maximum amount you can lose on one trade before entering. Investopedia’s “2% rule” describes limiting risk on any single trade to a small percentage of total capital.
Many traders adapt that idea to 1–2% depending on experience, strategy variance, and market conditions. Walbi’s trading lesson presents capital preservation strategies through disciplined percentage risk to reduce damaging equity swings.
Position size is the control knob that makes the rule real. If the stop distance increases, the position must decrease, or your risk silently expands. Some sources define position sizing as choosing how many units to trade to control risk and outcomes.
A practical sizing workflow links three inputs: account equity, risk percentage, and stop-loss distance. Risk amount equals equity multiplied by your chosen risk percentage, then divided by stop distance.

Key Point:
A risk per trade rule is only effective when the position size is recalculated from the stop distance. Otherwise, the “rule” becomes a guess, especially when volatility changes quickly.
Stop-Loss Logic and Loss Mitigation Strategy for Equity Curve Protection
Stop placement should be based on market structure and volatility, not on emotional comfort. A volatility-aware stop acknowledges that noisier markets require wider protective levels.
Investopedia explains that volatility stops can use ATR multiples to place stops at distances suited to recent movement.
Once the stop distance is chosen, position sizing must be adjusted to keep risk constant. This links stop-loss logic directly to capital preservation formulas and prevents accidental overexposure.
It is the practical bridge between capital protection trading and consistent execution under stress.
A loss mitigation strategy should include rules that limit how losses cluster. Common tools include hard stops, time stops, and daily loss limits that pause trading after a threshold.
These controls support equity curve protection by limiting damage from “bad days” and execution errors.
Q: Should I move a stop-loss when the trade is going against me?
A: Moving it wider usually increases risk beyond the plan, unless position size is reduced immediately. Volatility-based stops are designed before entry, so adjustments should follow rules rather than discomfort.
Drawdown Control in Capital Preservation
Drawdown control is the centre of capital preservation in trading because it protects the account’s ability to keep trading through losing phases. The goal is not avoiding losses entirely, but keeping losses small enough to recover without excessive risk-taking.
Maximum drawdown is widely defined as the peak-to-trough decline over a chosen period, expressed as a percentage.
Morningstar describes maximum drawdown as the decline from peak to trough during a specific period.
Robeco similarly defines maximum drawdown as the peak-to-trough decline and highlights its use as a risk indicator.

Key Insight:
When growth targets ignore drawdown limits, traders often increase leverage after losses, which accelerates account failure.
Maximum Drawdown Limit and Why Traders Must Define It
A maximum drawdown limit is a rule that caps how far equity can fall from a peak before you must reduce risk. It turns “I will manage risk” into a measurable boundary, which improves discipline under stress.
Capping drawdown supports preservation of capital because deep drawdowns change behaviour, not just account size. Once losses feel urgent, traders often break the risk per trade rule, increasing the chance of a spiral.
A predefined limit also clarifies whether you are operating in “capital preservation vs growth” mode. When volatility rises or execution slips, a lower drawdown limit shifts you toward preservation automatically.
Why does drawdown recovery become harder as losses deepen?
Drawdown recovery is asymmetric because the base shrinks after losses. A 20% loss needs a 25% gain to return to break-even, because gains apply to reduced equity.
This is why the best way to preserve capital is by avoiding large drawdowns rather than chasing bigger wins. As drawdowns deepen, recovery demands higher risk, which increases the risk of ruin for many strategies.
| Drawdown from peak | Required gain to recover |
|---|---|
| 10% | 11.1% |
| 20% | 25.0% |
| 30% | 42.9% |
| 40% | 66.7% |
| 50% | 100.0% |
Q: Is maximum drawdown the same as volatility?
A: No, volatility measures fluctuation, while maximum drawdown measures the single worst peak-to-trough decline.
Equity Curve Protection Rules and When to Reduce Risk
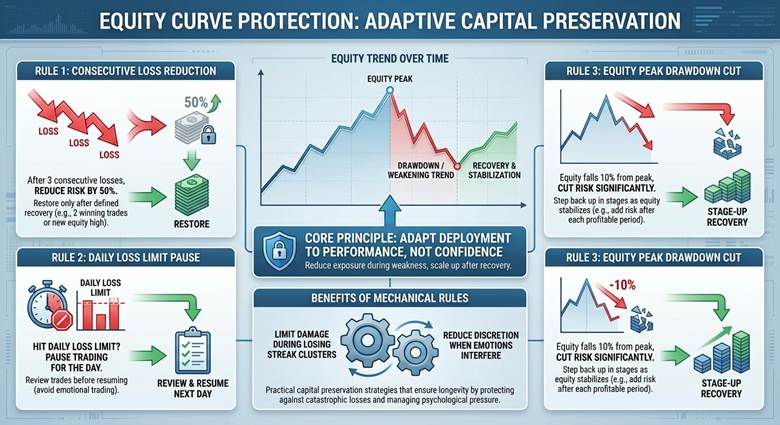
Equity curve protection means reducing exposure when your equity trend weakens, then scaling back up after recovery. It is a capital preservation method that adapts position size to performance, not to confidence.
A simple approach is a step-down risk after consecutive losses or after an equity break below a threshold. This is a practical form of capital preservation strategies because it limits damage during losing streak clusters.
Examples of rules traders use for drawdown control are intentionally mechanical. They reduce discretion when emotions are most likely to interfere with execution.
- Reduce risk by 50% after 3 consecutive losses, then restore only after a defined recovery.
- Pause trading for the day after a daily loss limit is hit, then review trades before resuming.
- Cut risk when equity falls 10% from peak, then step back up in stages as equity stabilises.

More Info:
Strategy drawdown comes from edge and variance, even with perfect execution, and it appears in backtests.
Risk of Ruin in Trading and Capital Preservation Strategies Traders Ignore
Risk of ruin is the probability that your account hits a defined failure level before your edge can recover losses. It rises when the risk per trade rule is too high, because losing streaks compound faster.
According to backtestbase, Risk of ruin helps answer a simple question: can your account survive normal variance without breaking rules?
That makes it central to capital preservation in trading, especially during drawdown control and equity curve protection phases.
Calculators exist, but assumptions matter more than the output number you see. BacktestBase notes common models assume fixed fractional sizing and independent trades, which real trading often violates.
Q: What inputs matter most in a risk of ruin estimate
A: Risk per trade, your edge assumptions, and the ruin threshold matter most because they dominate tail risk.
Capital preservation asset allocation in practice
A capital preservation portfolio for traders separates “trading float” from “reserve capital” to reduce forced decisions during drawdowns. This is a practical capital preservation method that supports an account survival strategy when volatility spikes and liquidity tightens.
The trading float funds active positions and absorbs normal losses within your maximum drawdown limit. The reserve sleeve protects continuity, so you can reduce exposure without liquidating positions at the worst moment.
Reserve capital should prioritise liquidity and low volatility rather than chasing yield. Money market funds are designed around short-term, high-quality instruments with safety and liquidity as primary objectives.

Key Insight:
A cash buffer reduces forced liquidation risk during drawdown control because it can absorb margin and collateral shocks.
| Style | Trading float | Reserve capital | Purpose of the reserve sleeve |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conservative | 30–40% | 60–70% | Maximum stability and liquidity during adverse regimes |
| Balanced | 50–60% | 40–50% | Flexibility to step down risk without stopping completely |
| Active trader | 70–80% | 20–30% | Minimal buffer, mainly to prevent forced exits |
Capital Preservation Formulas for Traders
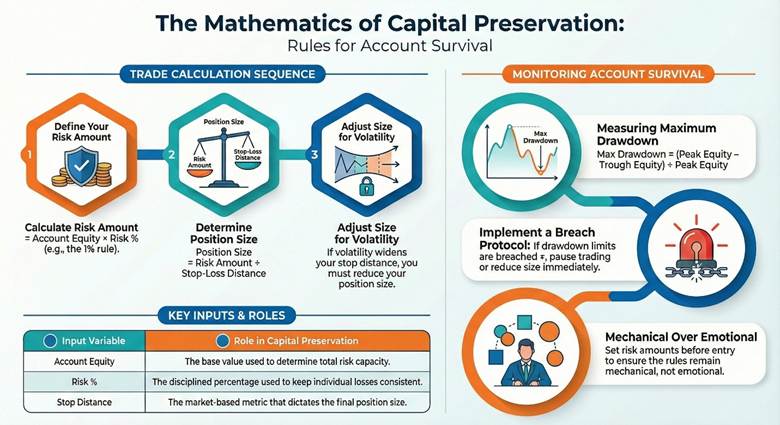
Capital preservation in trading becomes practical when risk rules are converted into repeatable numbers. These simple formulas support drawdown control, equity curve protection, and a consistent risk per trade rule.
Risk Amount Formula Using the 1% Rule Approach
Risk amount = Account equity × Risk %.
Walbi’s lesson frames this as a disciplined way to keep losses small and consistent. If your equity is £10,000 and the risk is 1%, the risk amount is £100. This supports the preservation of capital because one trade cannot dominate your monthly results.

Key Point:
Set the risk amount before entry; the risk per trade rule becomes emotional, not mechanical.
Position Size Formula Linked to Stop Distance
Position size = Risk amount ÷ Stop-loss distance.
TMGM presents the same sizing logic as dividing risk by stop distance to control loss size. Stop distance must be measured in the instrument’s units and then converted into cash risk. If volatility widens the stop distance, the position size must fall to preserve risk.
Maximum Drawdown Formula for Account Survival
Maximum drawdown measures the worst peak-to-trough fall in equity over a period. maximum drawdown as the peak-to-trough decline, typically shown as a percentage.
Maximum drawdown = (Peak equity − Trough equity) ÷ Peak equity.
Wall Street Prep explains this calculation using the peak and trough values from the equity curve.
A maximum drawdown limit turns this metric into a capital preservation method. When breached, you reduce size, pause trading, or switch to a lower-risk mode.
Q: What inputs matter most when using capital preservation formulas
A: Account equity, risk %, and stop distance matter most because they directly determine position size and loss size.
conclusion
Capital preservation in trading works best when every trade is sized from a fixed risk rule and enforced by hard drawdown limits. Using a position size calculator helps convert your stop distance into consistent exposure, which strengthens equity curve protection.
This discipline reduces emotional decision-making during losing streaks and improves long-term account survival. When preservation is systematic, growth becomes a by-product of controlled risk rather than aggressive leverage.






























