The hidden costs of forex trading can affect your profits and losses more than you might realize. One of the most important of these costs is the spread, a key concept that every trader needs to understand well. The spread shows the cost of opening a trade, and its type and broker conditions can significantly influence your overall trading strategy.
In this article, we go beyond the basic definition to explain the role of spreads in forex trading. We examine different types of spreads and how they influence trading style and decision-making in the forex market.

- If the spread is more than 10% of the average volatility of a trading pair, it may indicate that short-term entries are inefficient.
- During major news releases, even reputable brokers may temporarily widen spreads several times, so it’s best to avoid trading during these periods.
- The quoted spread is not always equal to the actual trading cost. To calculate the effective spread, you also need to account for execution delay and slippage.
What Is a Spread and How Is It Calculated?
The spread is the difference between the bid price and the ask price of a currency pair or trading asset. It represents the initial cost a trader pays when opening a position. In simple terms, the spread is how brokers earn money when a trade is executed. Because of this, professional traders always try to trade with lower spreads.
In MetaTrader, spreads are displayed in pips or points and may be fixed or variable. This cost is immediately reflected in the trade’s unrealised profit or loss. When a buy trade is opened, price must move by the spread to reach breakeven. As a result, spreads strongly influence broker choice, account type, and trading strategy decisions.
Is a lower spread always better for traders?
Not always. A low spread is valuable only if execution speed, slippage control, and order filling quality are also reliable.

How Is ُSpread Calculated?
Formula for Calculating Spread:
Spread = Ask – Bid
For example, if the EUR/USD pair has an ask price of 1.1050 and a bid price of 1.1048, the spread is 2 pips. In more precise account types, such as ECN accounts, this difference can be as little as 0.1 pip.
According to investopedia: The spread essentially functions as a “hidden commission” or transaction fee integrated directly into the trading price, allowing traders to avoid a separate, explicit commission fee.

The Bid and Ask prices, and consequently the spread amount, can vary significantly among different brokers based on their liquidity providers and order execution models.
Types of Spreads in Forex
Spreads in the forex market are generally divided into two main types, each with its own characteristics suited to different trading styles.
- fixed spread, which is commonly offered in market maker accounts.
- floating (variable) spread, which is typically found in accounts with direct market access, such as ECN accounts.
Understanding the difference between these two types can help traders manage their trading costs more effectively and make better decisions during volatile or high-risk market conditions. Many brokers allow clients to choose between these two account types, but making the right choice requires a clear understanding of one’s trading style and market behavior.
Below, we will take a closer look at each type of spread in forex trading:
Fixed Spread
A fixed spread is a predefined value that remains constant during trading hours. It is set by the broker and typically offered in market maker (dealing desk) accounts. The main advantage of a fixed spread is its stability, even during volatile market conditions.
Traders who avoid news-based or time-sensitive strategies often prefer fixed spreads. This is because the risk of sudden spread spikes is relatively low. However, fixed spreads are usually higher than floating spreads under normal market conditions.
During calm markets, fixed spreads can be more expensive than floating ones. In highly volatile periods, their price stability becomes a significant advantage. Overall, fixed spreads suit traders who prioritise predictable and consistent trading costs.


On trading platforms that provide Level II order book data, a sudden widening of the spread along with reduced market depth on one side (Bid or Ask) can signal a potential price move in the opposite direction.
Floating Spread
A floating spread, also known as a variable spread, changes in response to market supply and demand. It is the dominant spread type in accounts connected directly to liquidity providers. Brokers using ECN (Electronic Communication Network) or STP (Straight Through Processing) models aggregate quotes from multiple liquidity providers, and the spread fluctuates based on real-time market conditions.
When trading volume and liquidity are high, floating spreads can shrink to extremely low levels, sometimes close to zero pips. This environment is ideal for professional traders and scalpers. However, during critical events such as major economic news releases or sudden market shifts, floating spreads can widen sharply, which can work against traders.
Those who trade in fast or volatile markets should be prepared for spread widening and use tools like spread indicators and automated alerts to manage their positions more effectively.
Can floating spreads be predicted?
While exact spreads cannot be guaranteed, analyzing historical liquidity patterns, trading session overlaps, and news calendars can help anticipate likely spread behavior.
What Is a Zero Spread?
A zero spread account is a marketing term used by some brokers to attract professional or high-volume traders. On the surface, there appears to be no difference between the bid and ask prices, or the average spread is less than 0.1 pip. In reality, the broker compensates for this “zero” spread by charging a fixed commission per trade.
Zero-spread accounts are typically available on ECN platforms and are designed for traders who execute large volumes or use algorithmic or high-frequency strategies. The key point is that even if the spread is zero, the total trading cost must be calculated, since the combined commission and other fees can sometimes exceed the cost of a low-spread account.
This type of account is ideal for scalpers, trading bots, and algorithmic traders who rely on small price differentials. Still, it’s essential to carefully review the broker’s fee structure to ensure the account is truly cost-effective.


Even in accounts advertised as having "Zero Spread" (from 0.0 pips), the spread is never absolutely zero and will always be marginally above zero in reality, with the broker compensating via commission.
The Difference Between Spread and Commission
At first glance, spreads and commissions might look like the same kind of trading cost, but in reality, they are two completely different structures.
As explained earlier, the spread is the difference between the ask (buy) and bid (sell) prices of a trading instrument. Simply put, when you open a position, you start with a small loss equal to the spread. The spread is an indirect or hidden cost, while the commission is a fixed amount that the broker charges for each trade based on its volume. This model is common among ECN and STP brokers, where spreads are very tight or even close to zero, but the broker charges a set commission instead.
The key difference is that the spread changes with market liquidity and volatility, while the commission usually stays fixed. Because of this, traders need to choose which pricing model fits their strategy better, depending on whether a lower spread or a lower commission benefits them more.
| Feature | Spread | Commission |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The difference between the Ask (buy) and Bid (sell) price of a trading instrument | A fixed fee charged by the broker per trade based on trade volume |
| Cost Type | Indirect / hidden | Direct / explicit |
| Variability | Changes with market liquidity and volatility | Usually fixed, unaffected by market fluctuations |
| Common Model | Market Maker accounts (sometimes combined with commission) | ECN / STP accounts (with very tight or near-zero spreads) |
| Best Suited For | Scalpers and short-term traders in high-liquidity markets | Long-term traders or algorithmic strategies that benefit from fixed costs |
| Combination | Can be combined with a commission | Can be combined with a spread or standalone |
Some brokers only charge one of these fees, but many trading accounts include both spread and commission. To get a clear picture of your real trading cost, you need to consider both.
When choosing a broker or account type, scalpers and short-term traders often prefer accounts with low spreads and fixed commissions, while swing and position traders may find commission-free accounts with wider spreads more suitable and easier to manage.

Factors Affecting the Spread in Forex
The size of the spread in forex trading depends on various factors, each of which can cause sudden or gradual changes in the spread level. Understanding these factors is crucial for managing trading costs effectively.
The first factor is market liquidity. Currency pairs with high trading volumes generally have lower spreads. For example, EUR/USD or USD/JPY have tighter spreads due to high supply and demand.
The second factor is market volatility. When the market experiences sudden excitement, such as during the release of major economic data or interest rate announcements, spreads increase rapidly. This sudden increase, sometimes referred to as spread widening, can lead to stop-loss triggers or undesirable trade entries.

Some brokers use algorithmic filters to prevent algorithms from exploiting temporary decreases in spread, such as during news releases. These filters block trades when spreads are unusually low.
Another factor is the account type and broker model. In ECN accounts, spreads are floating and very competitive, but they come with a fixed commission. In contrast, market maker accounts offer fixed spreads, which are usually higher than the true market spread.
Trading hours also play a significant role. During the London-New York overlap, spreads are typically at their lowest, while in times of lower liquidity, such as during the night, spreads tend to widen.
Lastly, technology and execution speed are also important. Brokers with weak infrastructure or non-realistic models often offer unrealistic or unstable spreads. Therefore, paying attention to the broker’s reliability is key to predicting and managing spread fluctuations.
The Right Spread for Different Trading Styles
Each trading style requires a specific type of spread. Simply put, there is no one-size-fits-all solution for all traders. Below, we discuss the ideal spread for each type of trader:
Traders who use scalping or short-term trading strategies need very low spreads and accounts with fast execution. In such cases, even a 1 pip difference can make the difference between profit and loss. For this group, ECN accounts with spreads close to zero are ideal, provided the commission is reasonable as well.
| Trading Style | Spread Requirement | Preferred Account Type | Key Considerations / Tips |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scalping / Short-Term Trading | Very low (0–0.5 pips) | ECN | Execution speed is crucial. Even 1 pip can impact profit. Ensure commissions are reasonable. |
| Swing / Long-Term Trading | Moderate | Fixed or Floating | Less sensitive to spreads. Prioritize price stability and predictable broker behavior over minimal spread. |
| News-Based Trading | Stable / Low | Fixed Spread | Avoid trading during major economic releases to prevent sudden spread widening. Fixed spreads offer consistency. |
| Weekly Market Open | Can spike | Any | Spreads often widen at market open due to low liquidity and weekend price gaps. Plan entries carefully. |
On the other hand, swing traders or those focused on long-term trading are less sensitive to spreads. Since their goal is to make larger profits over a period of days or weeks, they can use accounts with slightly higher spreads without disrupting their strategy. For them, price stability and broker behavior predictability are more important factors.
For news-based traders, the spread should remain as stable as possible during major data releases. As a result, some traders prefer accounts with fixed spreads to avoid sudden spread widening during market volatility. However, this stability comes at a cost, as fixed spreads are usually higher than floating spreads under normal market conditions.
According to babypips, spreads widen sharply at the weekly market open on Sunday or Monday morning. This happens because of price gaps and low liquidity caused by news or events during market closure.
Which Currency Pairs Have the Lowest Spreads?
The major currency pairs, commonly referred to as the Majors, usually have the lowest spreads in the forex market. The main reason is the extremely high trading volume and liquidity these pairs offer.
The most popular and liquid pair is EUR/USD, which typically has a spread of around 0.1 to 1 pip under normal market conditions. In ECN accounts, this spread can sometimes drop to nearly zero.
Another pair with very tight spreads and stable price movements is USD/JPY. It is often considered ideal for traders who seek a balance between low spreads and precise technical behavior.
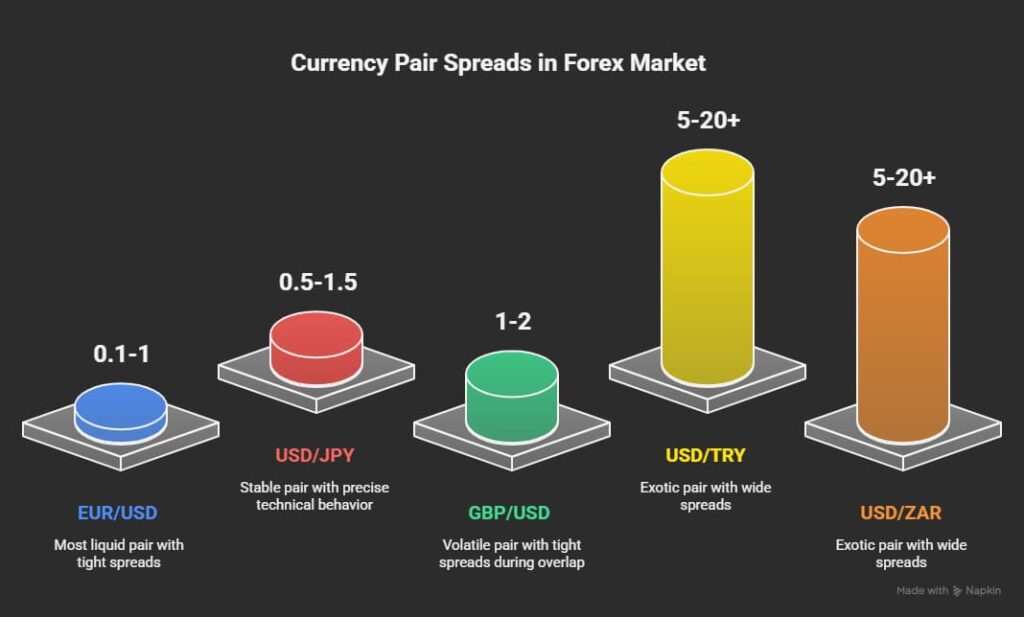
GBP/USD tends to show higher volatility, but during the London and New York session overlap, it often offers a tight spread, making it an attractive choice for scalpers.
In contrast, minor and exotic pairs such as USD/TRY or USD/ZAR have much wider spreads. Due to lower liquidity, higher risk, and unstable economic conditions in their respective countries, these spreads often range between 5 and 20 pips, and sometimes even more.
Overall, traders who aim to minimize trading costs should focus on major currency pairs and trade during active market hours to take advantage of the lowest possible spreads.
How Do Brokers Earn from Spreads
Forex brokers have several sources of income, and the spread is one of their main revenue streams. By adding a few tenths of a pip to the real bid and ask prices, brokers earn a profit from every trade. Even if a trader makes no profit or ends up losing money, the broker still collects its share through the spread.
In market maker accounts, this profit is earned directly. The broker acts as the counterparty to the trader’s position and applies its own predefined spread. This means the broker’s profit from each trade is guaranteed regardless of the trade outcome.
In ECN accounts, the broker acts as an intermediary. It receives price quotes from liquidity providers and passes them on to traders without adding any markup. In this model, the broker’s main income comes from a fixed commission per traded lot rather than from the spread itself.

It is important to note that brokers offering more competitive spreads usually work with a larger number of liquidity providers. The more sources they connect to, the closer their quotes are to the real market price and the tighter the spreads become.
Competition among brokers to attract clients often results in very low or even zero spreads. However, traders should always make sure that the quality of order execution and the absence of slippage are also maintained, since low spreads alone do not guarantee better trading conditions.

In certain high-liquidity conditions, the spread between the bid and ask prices can briefly turn negative for just a few milliseconds. This creates a rare arbitrage opportunity that can only be exploited in prime accounts with ultra-fast execution speeds.
Which Broker Offers the Lowest Spreads
Choosing a broker with low spreads is one of the most critical steps when entering the forex market. Many brokers claim to offer tight or even zero spreads, but in reality, there are important differences that can only be identified through careful analysis. The first factor to consider is the broker’s pricing model.
Brokers that operate under the ECN model generally provide the lowest possible spreads because they are directly connected to liquidity providers. However, these accounts usually include a fixed commission per traded lot as part of the cost structure.
Some well-known international brokers, such as Aron Groups, offer accounts with very low or near-zero spreads to stay competitive and attract more traders. These accounts are particularly suitable for scalpers, algorithmic traders, and high-volume traders. Still, it is essential to evaluate other factors such as execution quality, platform speed, technical support, and financial transparency alongside the spread level.
Many traders overlook that brokers can temporarily widen spreads during major news events or at market session openings and closings. Understanding these dynamics helps traders avoid unnecessary costs and choose brokers that maintain stable and transparent pricing across all market conditions.
Lowest Gold Spreads Among Brokers
Gold is one of the most popular assets in the forex market, but its spread is usually higher than that of currency pairs. This is mainly due to its high volatility and unique liquidity structure. In standard accounts, the spread on gold can range from 20 to 50 pips, which can significantly reduce potential profits in short-term trades.
However, some brokers, especially those catering to professional traders, offer tight-spread accounts for XAU/USD (gold versus the US dollar). In these accounts, the spread can drop to less than 10 cents. Such conditions are usually available in ECN accounts that include a separate commission fee. Brokers with direct connections to major liquidity providers are typically able to deliver more competitive pricing and lower spreads as a result.
In addition to the spread, traders should also consider factors such as execution speed, price slippage, and server stability, since gold trading often occurs in highly volatile and high-risk conditions. Those who focus on trading gold should choose a broker that not only offers low spreads, but also provides deep market liquidity, transparent data, and real-time analysis. Without these factors, a low spread alone can easily lose its advantage due to poor order execution quality.
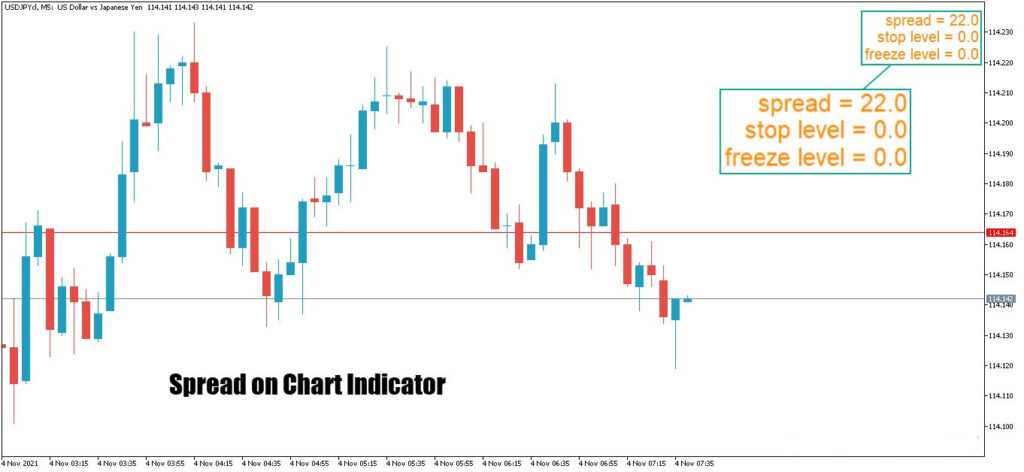
Spread Indicator for MetaTrader
The MetaTrader platform does not display the spread by default, but this limitation can be easily fixed by adding a spread indicator. This tool is essential for traders who want to make more precise decisions about their market entries and exits. Spread indicators show the current spread of each symbol directly on the chart in real time, and many of them also display the highest and lowest spreads recorded over a selected period.
In both MetaTrader 4 and MetaTrader 5, there are various types of spread indicators that can be downloaded and installed from reliable sources. Some versions include sound or text alerts that notify the trader when a sudden spread increase occurs. This feature is particularly valuable for scalpers and time-sensitive traders, as even a few seconds of delay in detecting spread changes can lead to a loss.
More advanced versions of these indicators can be integrated with other market data. For example, some versions display the spread alongside candle closing time and trading volume. Installing a spread indicator allows traders to monitor hidden market fluctuations and micro changes in liquidity, helping them make more informed and timely trading decisions.
Can spread indicators detect broker-specific execution anomalies?
Yes. Unusual or inconsistent spreads can indicate slippage risk or delayed order execution, helping traders choose more reliable brokers or accounts.
The Impact of Market Timing on Spread Fluctuations
The spread in the forex market is directly influenced by trading volume and liquidity conditions, both of which depend heavily on market hours. During the overlap of major sessions, such as the London and New York markets, trading volume reaches its peak, causing spreads to narrow to their lowest levels. In contrast, during quiet hours, such as late at night in global time, spreads tend to widen.
Spreads also fluctuate during market openings. For example, at the start of the trading week (Sunday night GMT), spreads temporarily increase until liquidity stabilizes. New traders often overlook these changes and enter positions within the first few minutes of the market opening, when spreads can be several times higher than normal.
Having a clear understanding of high-volatility and low-activity trading hours allows traders to enter the market at optimal times and minimize the cost of spreads. Using market session timing indicators, combining them with spread indicators, and maintaining time discipline are all key elements in building a consistent and efficient trading strategy.
Conclusion
If until now you thought of the spread as just a simple number on your trading screen, you now know that this small figure can make a big difference in your overall trading results. The spread is where the broker’s profit begins and where your potential profit or loss is determined.
Choosing a broker with competitive spreads, understanding peak liquidity hours, and selecting the spread type that aligns with your trading strategy are all essential steps toward becoming a more professional trader.
Successful forex trading is not limited to technical or fundamental analysis. A clear understanding of key concepts like the spread is what truly separates an amateur trader from a smart and skilled one.































