In the world of financial decision-making, every choice we make involves a cost known as opportunity cost. But what is the opportunity cost exactly? It refers to the value of the next best alternative that we give up when we make a decision. For example, if you choose to invest in the stock of Company A, your opportunity cost could be the potential return you would have earned by investing in the stock of Company B. In this article, we will explore what opportunity cost is, its significance in financial decisions, and how to calculate and minimize it. Stay with us to understand how you can use this concept to make smarter investment and financial decisions.

- Opportunity cost refers to the benefit you lose by not choosing an alternative option.
- To accurately evaluate opportunity cost, it's essential to assess the costs and benefits of each option and compare them.
- Considering opportunity cost can help individuals and organizations make more profitable decisions.
- This lost benefit is an internal measure used for strategic planning and is not reflected in accounting profits or external financial reports.
What is Opportunity Cost and Why is it Important?
Opportunity Cost is the value of the next best alternative that you give up when making a decision. This concept is important because it forces individuals and businesses to evaluate the true economic cost of their choices.
In cost analysis, there are two types of costs:
- Explicit Costs: These are direct and measurable costs, such as wages, rent, and raw materials. These costs are recorded in a company’s financial statements.
- Implicit Costs: These are indirect and non-measurable costs, such as the time an entrepreneur spends setting up a business instead of working at another job where they could earn income.
Understanding and calculating opportunity cost in financial markets is more important than it may seem. This concept helps investors avoid emotional and hasty decisions and allows them to allocate their limited resources more efficiently.
For example, deciding between investing in stocks or in fixed assets like bonds should take into account the opportunity cost of each option and their potential returns. Without this consideration, a choice might be made that results in lower profits compared to other options.
In behavioral economics, ignoring opportunity cost can lead to “incomplete analysis.” This happens when people focus only on explicit costs and fail to consider implicit costs, which can lead to poor decisions.

Opportunity cost is not only the lost profit but also appears as an implicit cost in economic analyses, playing a key role in calculating the true economic profit of companies.
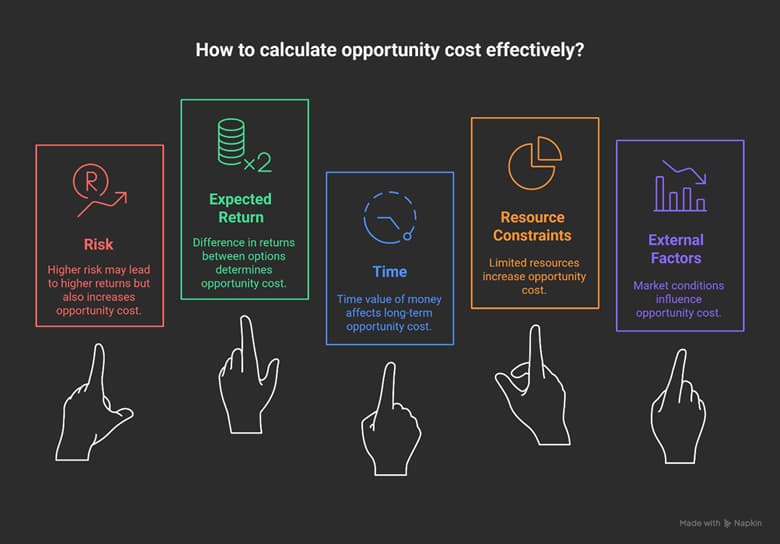
Factors Affecting Opportunity Cost
A clear understanding of how to calculate opportunity cost helps decision-makers make better choices and allocate their resources more efficiently. Several factors influence the level of opportunity cost, and we will explore the key ones here.
Risk
Risk is one of the key factors in calculating opportunity cost. The higher the risk of an investment, the higher the expected return must be for the investor to be willing to accept that risk. In such cases, opportunity cost increases because choosing lower-risk options means forgoing higher-risk opportunities that could potentially yield greater returns.
Expected Return
Calculating opportunity cost is closely tied to the expected return. The difference in returns between various options is a major factor in determining opportunity cost. For example, if one option offers a 10% return and another offers 5%, the opportunity cost of choosing the lower return option would be 5%. Essentially, choosing one option means forgoing the return from the other.
Time
Time is another significant factor in calculating opportunity cost. The time value of money means that money today is worth more than the same amount in the future. To more accurately calculate opportunity cost in long-term projects, a discount rate must be used to calculate the present value of future money. This is particularly important in financial analyses like project evaluations or when choosing between different investment options.
Resource Constraints
Resource constraints, such as budget, time, and human resources, have a significant impact on the calculation of opportunity cost. When resources are limited, decisions must be made in a way that maximizes returns from available resources. In this case, opportunity cost increases due to these resource limitations.
External Factors
External factors like inflation, market fluctuations, and interest rates can have a significant impact on opportunity cost. For example, in a low-interest-rate environment, the opportunity cost of investing in higher-risk assets might decrease because the returns from risk-free assets are lower, leading investors to be more inclined to choose higher-risk options.
In conclusion, to accurately and optimally calculate opportunity cost, all of these factors must be considered to make better choices and allocate resources effectively.
How to Calculate Opportunity Cost: Formula and Practical Example
To calculate opportunity cost, you first need to determine the difference in returns between two or more options. The simple formula we can use is:
Return of the Best Alternative Option – Return of the Chosen Option = Opportunity Cost
This formula helps us understand how much of the potential return from the best alternative option is lost by choosing one option over another. For example, let’s say you have $10,000 to invest and you consider two options:
- Option 1: Investing in stocks with a 10% annual return;
- Option 2: Investing in bonds with a 5% annual return.
If you choose the second option (bonds), your opportunity cost is the difference between the returns of stocks and bonds. In this example, your opportunity cost is 5%, or $500. This means that by choosing bonds over stocks, you are giving up $500 in potential gains.
To calculate opportunity cost more accurately, factors like risk and time should also be taken into account. For instance, in risk management, we can evaluate the return of each option based on its associated risk.
For more complex calculations and long-term projects, tools like Net Present Value (NPV) can be used. According to the Corporate Finance Institute, in financial analyses, opportunity cost is incorporated into the NPV formula using a discount rate to calculate the present value of future cash flows.

According to SmartAsset: To accurately calculate opportunity cost, the difference between the return of the chosen option and the return of the best alternative option must be calculated. This calculation helps investors make better decisions when allocating their financial resources.
Opportunity Cost in Investment
The concept of opportunity cost in investment helps you choose the option that provides the highest return with the least opportunity cost when making investment decisions. Simply put, it means choosing between different options and evaluating which one offers the highest profit for you.
Differences in Opportunity Cost of Various Assets: Stocks, Bonds, and Cryptocurrencies
Each type of investment has its own opportunity cost, depending on the risk and return. Stocks are high-risk but offer good returns. When the market is performing well, the opportunity cost of stocks is low because their return is higher than other options. For example, a large company’s stock, like Apple, might give a 15% return. Bonds, on the other hand, have low risk and offer fixed returns. However, when inflation is high, their opportunity cost increases because inflation devalues the fixed returns.
Cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin, are highly volatile, and their opportunity cost can be huge. The most famous example of opportunity cost is the trade of 10,000 Bitcoin for two pizzas in 2010. At that time, it was worth $41, but today, it would be worth over $970 million.
Methods for Analyzing Risk and Return for Better Decision Making
To calculate opportunity cost in investment effectively and make better choices, you should use analytical methods to evaluate risk and return. One such method is the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM).
This model helps you measure the risk of different investments and adjust the expected returns based on that risk. For instance, if you are considering investing in cryptocurrencies, which have high volatility, you should use this model to calculate the risk-adjusted return to ensure that the risk is adequately compensated by the return. In this context, fundamental analysis can help you assess the true value of assets and make better investment decisions.

In opportunity cost analysis, in addition to expected returns, the associated risks of each option must also be considered. Comparing the returns of different options without accounting for risk can lead to poor decision-making.
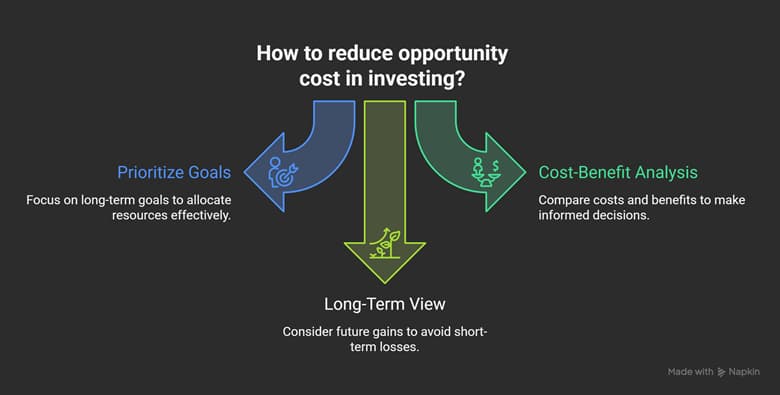
Practical Methods for Reducing Opportunity Cost
Opportunity cost occurs when you make a choice and forgo the benefits of other options. In the world of investing, the goal is to reduce this cost so you can make better financial decisions. This helps you use your resources more effectively and get the most out of each choice.
Prioritizing Goals and Resources
One simple method for reducing opportunity cost is to prioritize your goals. This means deciding which goal is most important to you and allocating your resources accordingly. For example, if your priority is saving for the future, it’s better to allocate your resources to investments that provide higher returns, such as stocks or real estate, rather than spending on unnecessary goods. To do this, you can use a decision matrix. This tool helps you rank your options based on your long-term goals, allowing you to minimize opportunity cost.
Using Cost-Benefit Analysis
Another method to reduce opportunity cost is by using cost-benefit analysis (CBA). This tool helps you compare the costs and benefits of each choice, allowing you to make more informed decisions. For instance, if you’re deciding between investing in stocks or gold, you should weigh the costs and potential returns of each option. Does the extra cost of buying and selling stocks justify the potential profit? Or is investing in gold with its fixed returns the better option? This comparison helps you become aware of the opportunity cost of each option and make a better decision.
Adopting a Long-Term View in Financial and Personal Choices
One of the best ways to reduce opportunity cost in investing is by adopting a long-term perspective. Instead of focusing only on short-term returns, consider what you can gain in the future. For example, investing in the S&P 500 over time could offer higher returns than holding cash or investing in low-risk assets. This choice can prevent the opportunity cost of holding cash and losing value due to inflation. In this process, paying attention to trading psychology can also help you avoid emotional decisions and make more informed choices.
Conclusion
In this article, we explored what opportunity cost is and how it can help you make better financial decisions. By gaining a clear understanding of this concept, you can make smarter choices and use your resources more efficiently. Calculating opportunity cost allows you to better evaluate the differences between various options and avoid decisions that could lead you to miss out on better opportunities. In the volatile world of financial markets, understanding this concept, especially in investment decisions, can play a significant role in your success.































