Blockchain technology, regarded as one of the most innovative inventions of the 21st century, has Revolutionised the way transactions are recorded and managed. At the core of this technology lies the concept of block height, which plays a crucial role in maintaining blockchain security and transparency.
Block height serves as an indicator of a block’s position in the blockchain, helping not only to track the history of transactions but also to ensure the integrity and security of the network. Understanding block height is key to grasping the underlying mechanics of blockchain technology, and in this article, we will explore the concept, how it is measured, its applications, challenges, and ways to monitor block height. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of its importance in the blockchain ecosystem.
Key Points:
|
What is Block Height and How is It Measured?
In blockchain technology, block height refers to the sequential number of a block in the blockchain. This number starts from the Genesis block (Block 0) and increases linearly with each new block added. Simply put, block height is the total number of blocks that have been created since the inception of the network.
Each block consists of two main parts: the header and the body. The block header contains information such as the timestamp (the precise creation time of the block), the hash of the previous block, and mining-related data. The body of the block holds the details of the transactions.
Calculating block height in the blockchain does not require a complex formula. It is simply the count of blocks produced since the Genesis block. This process is automatically handled by the nodes (network nodes). The block production time is determined by the consensus algorithm of each network. For instance, in Bitcoin, a block is created approximately every 10 minutes.
In summary, block height not only indicates the block’s position in the chain but also plays a critical role in the security and immutability of the network. The higher the block height, the harder it becomes to perform attacks, such as altering the transaction history.

| According to Investopedia, block height is sometimes calculated as the current length of the blockchain minus one. |
Why is Block Height Important in the Blockchain Network?
Block height is one of the most critical concepts in blockchain, contributing significantly to the security and integrity of the network. The importance of block height lies in its ability to indicate where a block is positioned within the Decentralised network. Block height plays an essential role in ensuring transparency and security in the blockchain through the following points:
- Transaction History: Each block acts like a page in a distributed ledger. Block height allows users to easily trace transactions all the way back to the Genesis block.
- Prevention of Manipulation: As block height increases, the cost of attacking the network (such as 51% attacks) grows exponentially because the attacker would need to modify the entire chain from the targeted block to the most recent block height.
Additionally, block height and network security are closely tied to the consensus algorithm. For example, in Bitcoin, a transaction is considered “secure” after it has been confirmed across 6 consecutive blocks (6 different block heights). This process makes the possibility of a transaction reversal almost zero.
| Block height is not only a record of the immutability of the blockchain, but it also ensures that all nodes in the Decentralised network agree on a single version of truth. |
Applications of Block Height in Blockchain Networks
Block height plays a significant role in various applications within blockchain networks, from ensuring security to enabling network upgrades. Here are some of the key uses of block height in blockchain ecosystems:
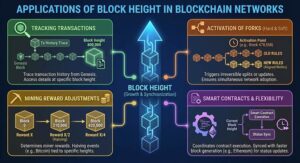
Tracking Transactions
Every transaction in the blockchain is tied to a specific block height. By using blockchain explorer block height tools, users can easily trace the history of any transaction, beginning from the Genesis block. For instance, if a transaction was recorded at Bitcoin block height 800,000, users can access all relevant details of that transaction within that block, including associated block confirmations.
Activation of Hard Forks and Soft Forks
Block height is crucial in activating both hard forks (irreversible splits) and soft forks (backward-compatible updates) in the blockchain. For example, the Bitcoin Cash hard fork took place at block height 478,558 in Bitcoin’s blockchain. This ensures all nodes in the network are aligned and adopt the new rules simultaneously, based on the specified block height.
Mining Reward Adjustments
Block height is used to determine the rewards for miners. In networks like Bitcoin, the reward for mining a block is halved every 210,000 blocks (approximately every 4 years). This event, known as “Halving,” is intrinsically tied to block height. As block height increases, miners also monitor the block confirmation process, ensuring that each block mined is secured against potential attack or manipulation.
Smart Contracts and Blockchain Flexibility
In blockchain networks like Ethereum, block height is used not only for transaction tracking but also for activating smart contracts. Due to Ethereum’s faster block generation time, block height plays a central role in ensuring that smart contract execution is synced with the blockchain’s growth and block confirmation times. The current block height helps developers and users understand the status of contracts and transactions within the network.
| According to Blockstream, block height is the numerical distance between a block and the very first block (the Genesis block), increasing by one each time a new block is added. |
Challenges and Limitations of Block Height
While an increase in the current block height indicates the growth of the blockchain network, it also brings about significant technical challenges. Some of these challenges include:
- Reduced scalability
- Stale block disruptions in network performance
- Node Synchronisation issues during updates and hard forks
- Hash dependencies in longer chains
Let’s explore each of these in detail:
Reduced Scalability
One of the main issues is scalability. As block height increases, the amount of data stored in the distributed ledger grows continuously, leading to higher processing demands on nodes. This can result in slower Synchronisation for new nodes or even cause some nodes to leave the network. The larger the block height, the more resources are required for maintaining the blockchain, which can significantly affect the scalability of the entire network.
Disruption of Stale Blocks in Network Performance
Stale blocks also affect network performance. A stale block is mined but not added to the main blockchain due to competition within the consensus algorithm. This phenomenon is common in networks with shorter block times, such as Ethereum, and can lead to wasted computational resources and decreased profitability for miners. As block height increases, the likelihood of stale blocks causing disruptions also rises.
Node Inconsistency in Updates and Hard Forks
Network updates and hard forks can also be challenging. Activating a network update or executing a hard fork requires consensus from nodes at a specific block height. If even a small number of nodes fail to update at the designated block height, the network can experience a split. For example, the Ethereum Classic hard fork at block height 1,920,000 faced challenges with node Synchronisation.

Hash Dependencies in Longer Chains
Additionally, the link between each block and the previous one via hashes increases with block height. The higher the block height, the greater the dependency on the hash mechanism, meaning even the smallest error in hashing calculations could cause significant disruptions throughout the entire network.
| Challenge | Explanation |
| Scalability | As the current block height increases, data becomes heavier, slowing down nodes. |
| Stale Blocks | Stale blocks slow data access and reduce network performance. |
| Network Update | Node synchronization at specific block height is difficult, and the network may split. |
How to Check Block Height?
To check and understand block height, you can use blockchain explorers. These tools, like Blockchain.com for Bitcoin or Etherscan for Ethereum, provide detailed information about block height.
Simply visit the blockchain explorer website and search for the block height number or the height of the latest block. The current block height shows where the most recent block is located in the blockchain, allowing you to compare it with previous blocks. These explorers also display the block time, which indicates the exact moment the block was created.
Hashing also plays a role in this process, as each block is identified by a unique hash. Some explorers even offer real-time tracking of block height and block times, which can help analyze transactions.

Conclusion
Block height serves as a key metric in blockchain, playing an irreplaceable role in ensuring the security and transparency of blockchain systems. This concept strengthens user trust in Decentralised systems by creating an immutable chain and allows for precise tracking of transactions. In the future, as blockchain applications expand into fields like finance, healthcare, and supply chains, block height will become even more important as an indicator for evaluating the sustainability and scalability of networks.
Technological advancements, such as second-layer solutions and new consensus algorithms, can reduce the challenges associated with block height and improve efficiency. This growth potential demonstrates that blockchain is not only transforming existing systems but also providing a foundation for future innovations that could redefine the digital economy.
































