In a world where personal data and financial transactions are rapidly exchanged in the digital space, how can we ensure their security? The answer lies in cryptography. This technology secures information by transforming it into unbreakable codes, ensuring the privacy and security of data.
Many ask, What is cryptography, and why is it so crucial? Rooted in the history of cryptography and humanity’s efforts to protect confidentiality, this field today sits at the heart of blockchain and cryptocurrencies. With cryptography securing data, online transactions are shielded from threats, and trust in digital networks is reinforced. This article will introduce you to the vital role of cryptography in modern technologies, explore its various types, and discuss its impact on the future. Continue reading to delve into the hidden world of digital security.
Key Takeaways:
|
What is Cryptography?
Cryptography is the science that protects information from unAuthorised access by leveraging mathematics and computer science. This technology works through encryption and decryption, converting data from plaintext to ciphertext, ensuring that only Authorised recipients can read it. The goals of cryptography include:
- Confidentiality to maintain secrets
- Data integrity to prevent tampering
- Authentication to verify identity
- Non-repudiation to prevent the denial of a message
The roots of cryptography date back to ancient times, when the Egyptians used hieroglyphs as codes, and Julius Caesar used the Caesar cipher for secret messages. In the 20th century, the Enigma machine became a prominent example of cryptography used during World War II.
Today, cryptography plays a crucial role in technologies such as cryptocurrencies, enabling secure transactions on blockchain. Through complex algorithms, cryptography strengthens digital security.

The Role of Cryptography in Blockchain Networks
Cryptography, or crypto, serves as the backbone of information security in deCentralised networks like blockchain. In this technology, data is stored not on a Centralised server but in a distributed ledger, maintained by thousands of nodes around the world. Cryptography creates a mathematical layer of protection, ensuring that no central entity is needed to validate transactions or maintain the cybersecurity of the network.
This technology uses techniques such as hash functions in blockchain and public key cryptography to protect user privacy and prevent unAuthorised access. The cryptographic system in blockchain ensures that transactions are only validated by Authorised individuals, while cryptography also enables privacy, allowing for anonymous transactions through encryption.
One of the most crucial features of blockchain is the immutability of data, achieved through hashing algorithms in blockchain such as SHA-256. Each block in the chain contains a unique hash that links to the previous block. This chain structure makes tampering with data almost impossible, as altering even a single transaction would require rewriting the entire chain, which is computationally impractical due to the immense resources needed.
Satoshi Nakamoto, the creator of Bitcoin, solved the double-spending problem by introducing cryptography into Bitcoin in 2008, revolutionizing blockchain technology. In Bitcoin, cryptography secures transactions through algorithms like SHA-256 and digital signatures in the blockchain, preventing fraud and ensuring data integrity.
This cryptographic system not only strengthens trust in deCentralised networks but also enables transparent and immutable data recording. Therefore, cryptography is the core of blockchain technology, guaranteeing its security and efficiency in both financial and non-financial applications.
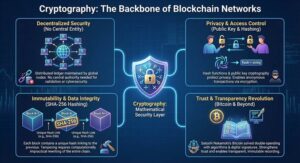
| According to GeeksforGeeks, “cryptography in blockchain secures transactions and makes data immutable, which is essential for building trust in deCentralised networks.” |
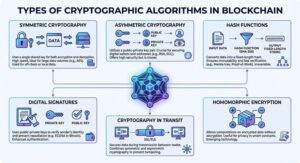
Types of Cryptographic Algorithms in Blockchain
In cryptography, or crypto, various algorithms are used to secure transactions and protect sensitive data. These algorithms create layers of security, enabling activities in deCentralised networks like blockchain. Below are the main types of cryptographic algorithms employed in blockchain technology:
Symmetric Cryptography
Symmetric cryptography uses a single shared key for both encryption and decryption. Due to its high speed, this method is ideal for encrypting large volumes of data, such as those stored in databases. Algorithms like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) are examples of symmetric cryptography.
Its advantages include speed and efficiency, but its main disadvantage is the secure sharing of the key. If the key is compromised, security is at risk. In blockchain, symmetric cryptography is often used for encrypting off-chain or local data, as sharing the key in open networks is challenging.

Asymmetric Cryptography
Asymmetric cryptography utilizes a pair of public and private keys, which are generated using complex algorithms. The public key is used for encryption, while the private key is used for decryption.
This method is crucial for securing digital wallets and addresses in cryptocurrencies. For example, in Bitcoin, public and private keys enable the signing of transactions and confirmation of ownership. Algorithms such as RSA and elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) are commonly used. Asymmetric cryptography offers high security but is slower than symmetric methods.
Hash Functions
A hash function in blockchain converts data into a fixed-length string called a hash, which plays a key role in the Merkle tree and proof-of-work algorithm. In Bitcoin, the SHA-256 algorithm generates irreversible hashes, ensuring immutability. The Merkle tree organizes transaction hashes, allowing for fast and efficient verification.
In proof-of-work, miners solve complex equations to generate valid hashes, helping to confirm blocks. This method prevents data manipulation, but may be vulnerable to future quantum attacks.

Digital Signatures
Digital signatures in blockchain are another form of cryptography that uses public and private keys to verify the sender’s identity and prevent repudiation. In blockchain, validators use digital signatures to verify transactions. For example, the ECDSA algorithm in Bitcoin ensures that only the wallet owner can sign a transaction. This method enhances authentication but depends on the secure management of private keys.
Cryptography in Transit
Cryptography in transit secures data as it is transmitted between blockchain nodes using protocols like SSL/TLS. These protocols combine both symmetric and asymmetric cryptography to protect sensitive data during transmission. For example, when a transaction is sent to the network, SSL/TLS prevents data tampering. This method is essential for secure communication but requires a strong infrastructure.
Homomorphic Encryption
Homomorphic encryption allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without decrypting it. This emerging technology is useful in blockchain for maintaining privacy in smart contracts. For example, financial data can be Analysed while still encrypted. However, due to the computational complexity, homomorphic encryption is not yet widely used but holds great promise for the future.
With these cryptographic algorithms, cryptography has turned blockchain into a secure and deCentralised system. From hash functions to homomorphic encryption, each method plays a unique role in protecting transactions and sensitive data.
Differences Between Symmetric and Asymmetric Cryptography
Symmetric cryptography and asymmetric cryptography are the two primary approaches in cryptography, each with distinct differences in terms of key structure, speed, security, and use cases:
- Speed:
- Symmetric cryptography (e.g., AES) is faster, as it uses a shared key for both encryption and decryption, making it ideal for encrypting large volumes of data (e.g., sensitive information in digital wallets).
- Asymmetric cryptography (e.g., RSA) is slower because of the computational complexity involved in using both a public and a private key.
- Security:
- Asymmetric cryptography offers stronger cybersecurity due to the separation of public and private keys, making it ideal for authentication in blockchain transactions or securing cryptocurrencies.
- Symmetric cryptography, while fast, becomes vulnerable if the shared key is exposed.
- Applications:
- Symmetric cryptography is typically used for encrypting internal system data.
- Asymmetric cryptography is primarily used for secure key exchanges or digital signatures in blockchain to verify transactions.
- Complexity:
- Asymmetric cryptography is more computationally expensive due to its complex mathematical foundations (e.g., large prime numbers), making it harder and more costly to implement compared to symmetric cryptography.
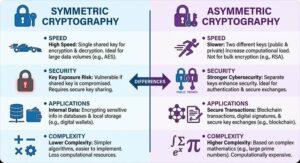
| In blockchain, combining both methods (such as using asymmetric cryptography for key agreement and symmetric cryptography for data transfer) is the most optimal solution. |
Examples of Cryptography in Cryptocurrencies
Cryptography, or crypto, is what makes cryptocurrencies secure and trustworthy. Here are a few simple examples of how it plays a crucial role:
- Every Bitcoin user has an address (similar to an account number), which is created from their private key. This key functions as a secret password that only the owner knows. When you make a transaction, Bitcoin confirms that you are the rightful owner of the asset by using a digital signature (which is a combination of the private key and public key).
Additionally, all transactions are hashed using the SHA-256 hashing algorithm in blockchain, turning them into immutable codes to prevent tampering.
- In Ethereum, cryptography employs the ECDSA algorithm (Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm) and sometimes Skitel for signing transactions, ensuring security and authentication. Other cryptocurrencies like Cardano also use public and private keys to secure transactions.
The recovery phrase in these networks is also critical for regaining access to funds.
These examples demonstrate the pivotal role that cryptography plays in protecting cryptocurrencies and ensuring their security and integrity.
Advantages and Limitations of Cryptography in Blockchain
Cryptography, or crypto, acts as a strong lock to protect blockchain networks. The advantages of cryptography are striking, as it provides high security to safeguard sensitive information and maintain the privacy of users.
For example, in blockchain, cryptography ensures that transactions are not tampered with and that data remains immutable. By using private keys and digital signatures in blockchain, only Authorised individuals can access information or perform transactions. This feature enhances trust in deCentralised networks like Bitcoin, giving users peace of mind.
However, the limitations of cryptography should not be overlooked. Some of the disadvantages include:
- Computational Complexity: Cryptographic algorithms sometimes require substantial energy and time, which can slow down the network or increase costs.
- Cybersecurity Threats: Hackers and attackers are always lurking, and cyberattacks, such as stealing private keys, can compromise security. If cryptography is not implemented correctly, vulnerabilities may arise that attackers can exploit. Therefore, precise design and regular updates to cryptography are crucial to combat these cyber threats.
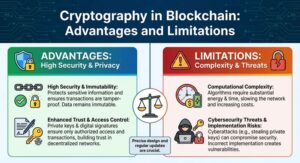
Below is a summary table highlighting the advantages and limitations of cryptography in blockchain:
| Advantages | Limitations |
| High Security: Protects data from unAuthorised access | Computational Complexity: Requires significant processing power and energy |
| Privacy: Ensures user anonymity and confidentiality | Cybersecurity Threats: Risks from hackers and attackers |
| Immutability: Prevents transaction and data manipulation | Design Flaws: Vulnerabilities due to weak implementation |
| Trust Building: Enhances trust in deCentralised networks | High Costs: Energy and resources required to run algorithms |
Quantum Cryptography
Quantum cryptography is an emerging branch of cryptography that leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to create security systems that are nearly unbreakable. In this method, information is encrypted using qubits (the fundamental unit of quantum processing), which, unlike classical bits, can exist in multiple states simultaneously.
This property makes quantum computing extremely powerful, but it also poses a threat to current cryptographic algorithms like RSA and elliptic curve cryptography (ECC), as quantum computers can break these systems in a short amount of time.
In blockchain, quantum cryptography blockchain can make transactions nearly impenetrable through techniques like quantum key distribution (QKD). The opportunities include higher security and faster processing speeds, but challenges such as the instability of qubits and the high costs of infrastructure remain barriers.
Despite these challenges, quantum cryptography has the potential to revolutionize the future of blockchain security, provided that quantum computing technology matures.

Conclusion
Cryptography is the cornerstone of blockchain security and the driving force behind DeFi (DeCentralised Finance). From hashing algorithms in blockchain to homomorphic encryption, this foundational technology enables transparency, decentralization, and resistance to tampering. Despite emerging threats like quantum computing, cryptography must evolve to continue supporting digital trust and innovation in smart contracts and deCentralised financial platforms. The future of the digital economy will be built on resilient algorithms and advanced cryptography.































