In the name of God
ICO (Initial Coin Offering)
In recent years, the world of cryptocurrencies has experienced a revolutionary funding mechanism known as Initial Coin Offering (ICO). ICOs have emerged as an alternative method for raising capital, allowing blockchain projects to bypass traditional venture capital routes and democratize investment opportunities. This article explores the concept of ICOs, their significance, and the challenges and opportunities they present in the ever-evolving cryptocurrency landscape.

_ Understanding ICOs :
ICO, short for Initial Coin Offering, is a fundraising method employed by blockchain-based projects to raise capital in the form of cryptocurrencies. Unlike traditional initial public offerings (IPOs), where investors receive shares in a company, ICOs offer investors tokens or coins associated with the project being funded. These tokens serve various purposes, such as accessing the project’s platform, utilizing its services, or representing a stake in the project’s future success.
_ ICO Process :
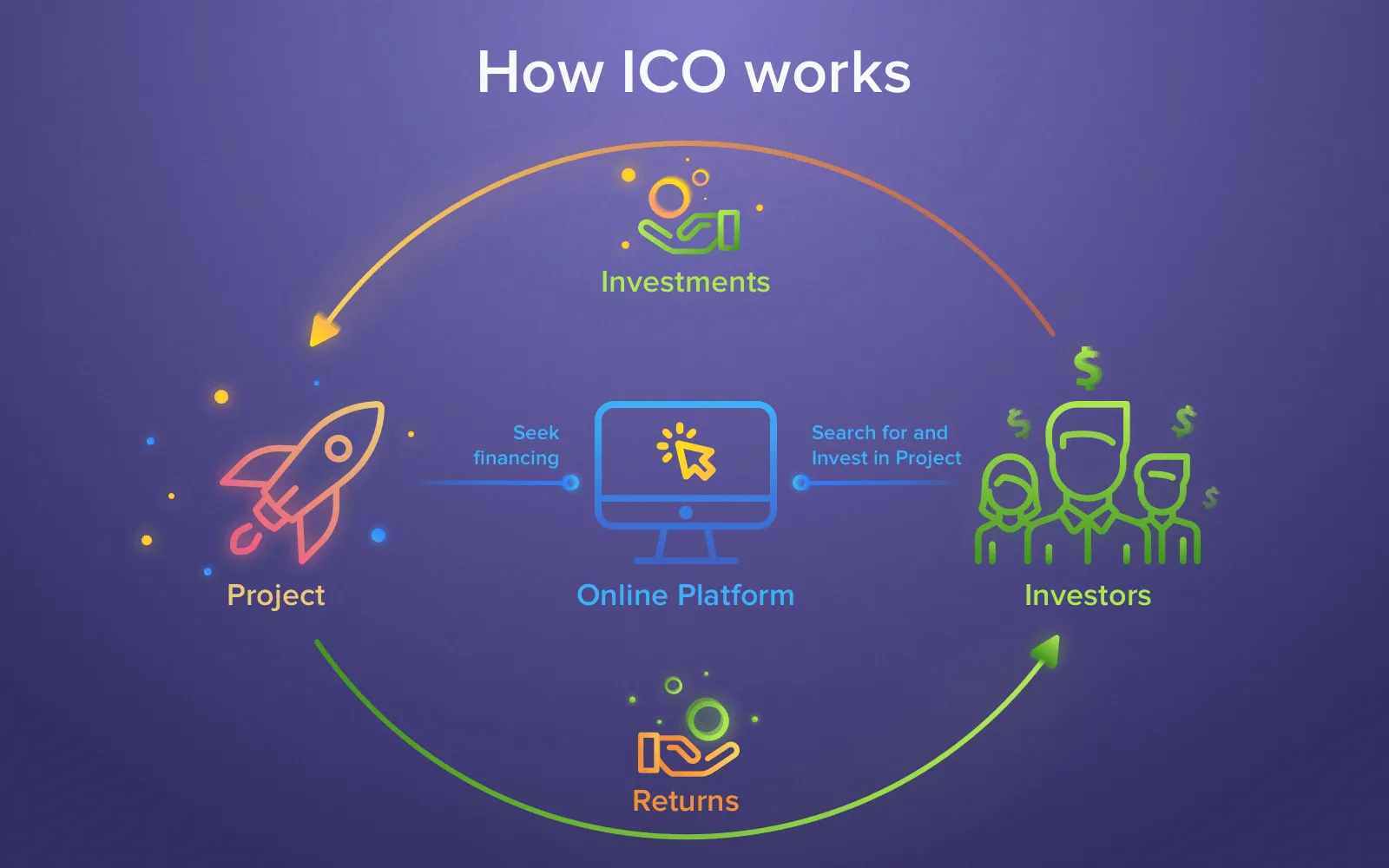
The ICO process typically involves several stages:
- Whitepaper: Blockchain projects seeking funding create a comprehensive whitepaper outlining their objectives, technical details, and implementation strategies. The whitepaper acts as a prospectus, providing potential investors with the necessary information to make informed decisions.
- Token Creation: The project’s team creates a new cryptocurrency or token that will be sold during the ICO. These tokens are often based on existing blockchain platforms like Ethereum (ERC-20 tokens) and are distributed to investors in exchange for established cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ether.
- Pre-sale and Crowdsale: The ICO is often divided into pre-sale and crowdsale phases. During the pre-sale, early investors and supporters are given the opportunity to acquire tokens at a discounted price. The crowdsale phase is open to the general public, allowing anyone interested in the project to participate.
- Token Distribution: Once the ICO concludes, the project distributes the purchased tokens to the investors’ wallets. These tokens can be traded on cryptocurrency exchanges or used within the project’s ecosystem, depending on their utility.
_ Benefits and Opportunities :
ICOs present several benefits and opportunities for both investors and blockchain projects:
- Access to Capital: ICOs provide a decentralized and inclusive funding mechanism, enabling projects to raise capital from a global pool of investors. This opens up opportunities for innovative projects that may have difficulty accessing traditional funding channels.
- Liquidity and Trading: Tokens acquired through ICOs can often be traded on cryptocurrency exchanges, providing investors with liquidity and the potential for profit if the project succeeds and the token’s value appreciates.
- Democratization of Investment: ICOs enable small investors to participate in early-stage funding, leveling the playing field and allowing retail investors to support projects they believe in. This democratization of investment opportunities is a significant departure from traditional venture capital models.
_ Challenges and Risks :
While ICOs have gained popularity, they also pose certain challenges and risks:
- Lack of Regulation: Unregulated ICOs raise concerns about investor protection and scams. Regulatory frameworks are being developed to address these issues.
- Investor Awareness: Due diligence is crucial when investing in ICOs, as the lack of regulation and oversight means investors must carefully evaluate projects for transparency, viability, and potential risks before committing capital.
- Market Volatility: The cryptocurrency market is highly volatile, and ICO tokens are not immune to price fluctuations. Investors must be prepared for the inherent risks associated with investing in a nascent and rapidly evolving market.

_ Alternative Funding Mechanisms for Crypto Projects (Beyond ICOs) :
- Security Token Offerings (STOs): STOs are fundraising events that involve the issuance and sale of security tokens, which represent ownership in an underlying asset or company. Unlike utility tokens in ICOs, security tokens are designed to comply with existing securities regulations. STOs provide a regulated and compliant alternative to ICOs, offering enhanced investor protection and legal certainty. By aligning with regulatory requirements, STOs aim to attract institutional investors who may have been hesitant to participate in the ICO market.
- Initial Exchange Offerings (IEOs): IEOs are token sales conducted on cryptocurrency exchanges. Unlike ICOs where projects independently market and sell their tokens, IEOs involve partnering with a specific exchange that facilitates the token sale on its platform. The exchange acts as a trusted intermediary, conducting due diligence on behalf of investors and providing a platform for token trading. IEOs offer benefits such as increased investor confidence, immediate liquidity, and a ready user base on the partnering exchange.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): DeFi refers to a rapidly growing ecosystem of decentralized financial applications built on blockchain platforms. DeFi platforms aim to provide traditional financial services such as lending, borrowing, trading, and yield farming in a decentralized manner, eliminating the need for intermediaries like banks. DeFi projects often utilize their native tokens to incentivize participation and govern the platform. While not specifically a fundraising mechanism, DeFi has created opportunities for project funding through mechanisms like Initial Liquidity Offerings (ILOs) and token sales on decentralized exchanges.
It’s important to note that while these alternative mechanisms have gained popularity, ICOs continue to be used for fundraising in the cryptocurrency space. Each mechanism has its advantages and considerations, and the choice between them depends on the project’s goals, legal requirements, and target investor base.
ICO funding has revolutionized the way blockchain projects raise capital, providing a decentralized and inclusive alternative to traditional venture capital. While ICOs have democratized investment opportunities and fueled innovation in the cryptocurrency space, they also come with challenges and risks. As the regulatory landscape evolves and investor awareness increases, ICOs have the potential to continue shaping the future of fundraising and the broader adoption of blockchain technology.































