In the name of God
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Networks in Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has revolutionized various industries by introducing decentralized and transparent systems. At the heart of this groundbreaking technology lies the concept of peer-to-peer (P2P) networks. P2P networks play a crucial role in facilitating the decentralized nature of blockchain systems, enabling secure and direct interactions between participants without the need for intermediaries. In this article, we will delve into the significance of P2P in blockchain technology and its impact on trust, collaboration, and data integrity.

_ Understanding P2P Networks :
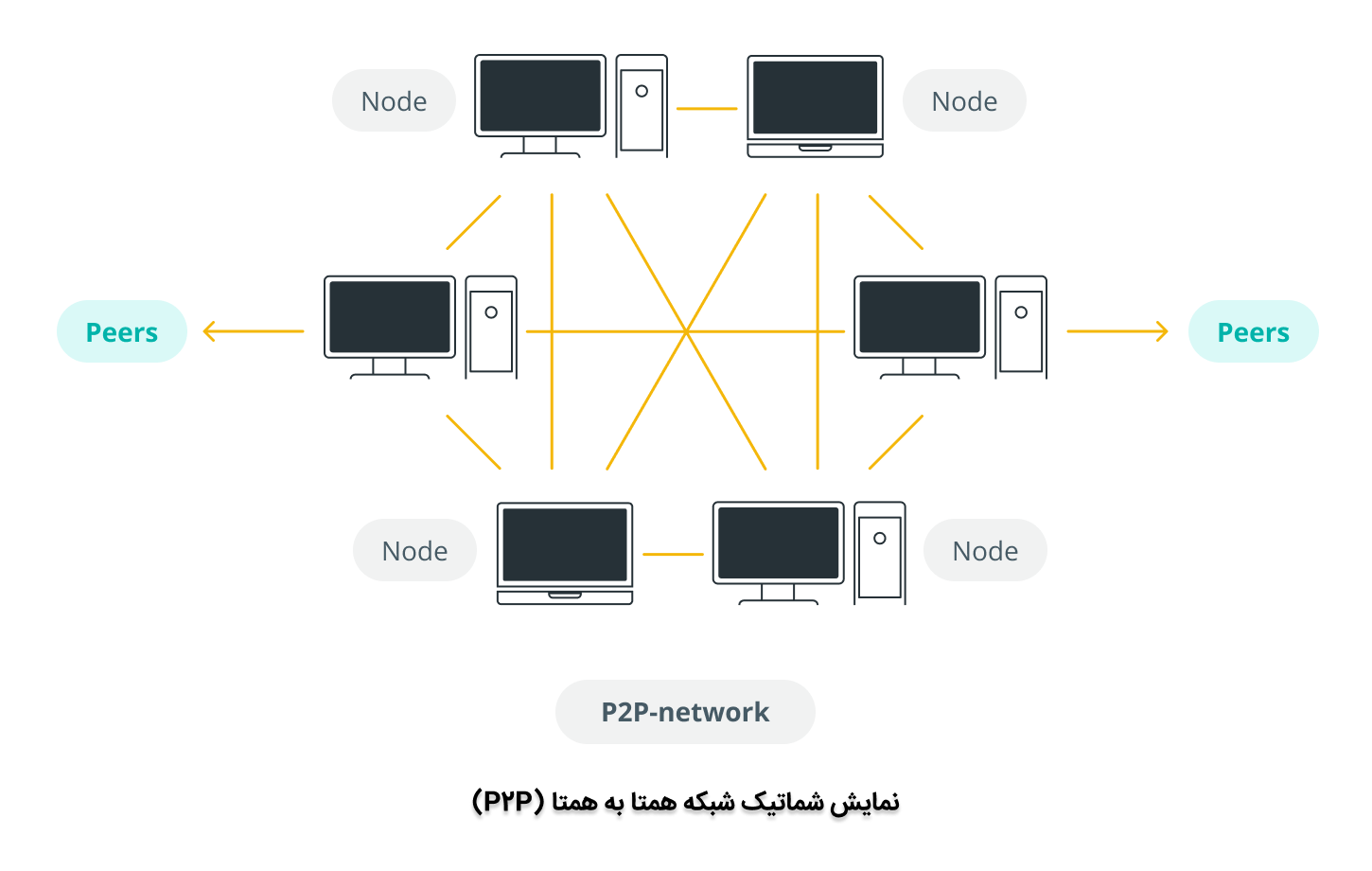
A peer-to-peer network is a distributed network architecture that allows individual participants, or peers, to interact directly with each other without relying on a central authority. Unlike traditional client-server models, P2P networks distribute both the data and the computational workload across all participating nodes.
In the context of blockchain technology, P2P networks form the backbone of the decentralized infrastructure. Each node in the network maintains a copy of the entire blockchain, and all nodes work collectively to validate and propagate transactions. This distributed approach ensures that no single entity has control over the network, making it resilient to censorship, tampering, or single points of failure.
_ P2P applications in blockchain technology :
Peer-to-peer (P2P) networks play a crucial role in various applications of blockchain technology. Here are some notable applications where P2P networks are utilized:
- Cryptocurrencies and Digital Assets: P2P networks are at the core of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. These networks enable participants to directly send and receive digital currencies without the need for intermediaries. Each participant in the network maintains a copy of the blockchain, verifying and propagating transactions through a consensus mechanism. P2P networks ensure secure and transparent transactions while eliminating the reliance on centralized financial institutions.
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEX): P2P networks are instrumental in the development of decentralized exchanges. These platforms allow users to trade cryptocurrencies directly with each other without the need for a central authority. By utilizing P2P networks, decentralized exchanges provide enhanced security, privacy, and control over assets, reducing the risk of hacks or manipulation associated with centralized exchanges.
- Distributed File Storage and Sharing: P2P networks are leveraged in blockchain-based distributed file storage and sharing systems. These platforms allow users to store and share files across a decentralized network of nodes. Instead of relying on a central server, files are divided into smaller encrypted fragments and distributed across participating nodes. P2P networks ensure data redundancy, availability, and censorship resistance, making them ideal for secure and resilient file storage.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain-based supply chain management systems utilize P2P networks to enhance transparency, traceability, and trust in the supply chain ecosystem. P2P networks enable direct communication and data sharing between different stakeholders, including manufacturers, suppliers, distributors, and consumers. By recording supply chain data on a shared and immutable ledger, P2P networks enable real-time tracking, authentication, and verification of products, reducing fraud, counterfeiting, and inefficiencies.
- Decentralized Governance: P2P networks are employed in blockchain-based decentralized governance models. These models aim to create transparent, open, and democratic systems for decision-making and governance. By utilizing P2P networks, participants can directly participate in voting, consensus building, and decision-making processes without relying on centralized authorities. P2P networks facilitate secure communication, consensus, and coordination among participants, enabling decentralized governance at scale.
- Identity Management: P2P networks are utilized in blockchain-based identity management systems to provide individuals with control over their digital identities. Instead of relying on centralized identity providers, P2P networks enable users to store their identity information on a blockchain and share it selectively with trusted entities. P2P networks ensure secure and tamper-proof identity verification, reducing the risk of identity theft or misuse of personal information.
- Internet of Things (IoT): P2P networks play a significant role in blockchain-based IoT applications. By combining IoT devices with blockchain technology, P2P networks facilitate secure and autonomous machine-to-machine communication, data sharing, and transactions. P2P networks enable direct interaction and coordination between IoT devices, eliminating the need for intermediaries and enhancing the security, privacy, and efficiency of IoT ecosystems.

_ Benefits of P2P in Blockchain :
- Decentralization and Trust: P2P networks eliminate the need for intermediaries, such as banks or governing authorities, by enabling direct transactions between participants. This decentralization fosters trust as it removes the reliance on a single party to validate and authenticate transactions. Instead, the consensus mechanism, often achieved through consensus algorithms like Proof-of-Work (PoW) or Proof-of-Stake (PoS), ensures agreement among participants, enhancing the security and integrity of the blockchain.
- Enhanced Security: P2P networks provide robust security mechanisms by distributing data across multiple nodes. Unlike centralized systems, where a single attack can cripple the entire network, blockchain networks are inherently resistant to attacks since an attacker would need to compromise a significant portion of the network to alter the blockchain’s integrity. This distributed nature of P2P networks significantly improves the security and resilience of blockchain systems.
- Improved Efficiency: P2P networks in blockchain technology eliminate the need for intermediaries, reducing time delays and costs associated with intermediaries’ involvement. Participants can directly transact with each other, streamlining the process and improving overall efficiency. Additionally, P2P networks enable faster data propagation and consensus, increasing the speed of transaction validation and reducing settlement times.
- Data Redundancy and Availability: Since each node in a P2P network maintains a copy of the entire blockchain, data redundancy is inherently built into the system. If a node fails or goes offline, other nodes can continue the network’s operation, ensuring high availability and fault tolerance. This redundancy makes blockchain systems highly resilient to data loss or censorship attempts.
_ Challenges and Considerations :
While P2P networks offer numerous advantages for blockchain technology, there are also some challenges and considerations to address:
-
- Scalability: As the number of participants and transactions increases, the scalability of P2P networks becomes a crucial concern. Blockchain systems, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, have faced scalability challenges, resulting in slower transaction processing times and higher fees. Various scalability solutions, including layer-two protocols like Lightning Network and sharding techniques, are being explored to address these challenges.
- Network Connectivity: P2P networks require participants to be connected to the network continuously. However, maintaining uninterrupted connectivity can be challenging, especially in regions with limited internet access or during network disruptions. Ensuring widespread network connectivity is essential for the success of P2P blockchain networks.
- Security and Privacy: While P2P networks provide enhanced security, participants must ensure the privacy and confidentiality of their data. Encryption techniques and privacy-focused protocols play a vital role in protecting sensitive information while maintaining the benefits of a decentralized network.

Peer-to-peer (P2P) networks are the foundation of blockchain technology, enabling decentralized trust, collaboration, and data integrity. By eliminating intermediaries and relying on distributed consensus mechanisms, P2P networks foster trust among participants and enhance the security and efficiency of blockchain systems. Despite challenges such as scalability and network connectivity, P2P networks continue to drive innovation in various industries, revolutionizing the way we transact, interact, and collaborate in the digital age.
Good luck
Saman































