Web3 is a revolutionary concept that envisions a Decentralised internet where users have full control over their data, identity, and digital assets, free from the dominance of tech giants. Built on blockchain technology, Web3 prioritizes privacy, security, and digital ownership, offering a new way to experience the online world. This article explores the fundamentals of Web3, including how it works, its benefits, leading projects, and potential challenges, and discusses how you can get involved and profit from this transformative shift in the digital landscape.
| key takeaways:
· In many Web3 projects, data is stored on Decentralised networks like IPFS or Arweave, rather than on Centralised servers. · Some Web3 wallets allow asset recovery through friend confirmation (guardian keys), eliminating the need for a recovery phrase. · Web3 creates complex, interconnected digital worlds by combining multiple layers of the metaverse, blockchain interoperability, and Decentralised data. · With the rise of quantum computing, Web3 projects are working on quantum-resistant encryption algorithms to ensure long-term security. |
What is Web3 and How Does it Work?
Web3 is the next generation of the internet, built on decentralization and the elimination of intermediaries. Unlike Web2, where platforms like Facebook and Google control user data and interactions, Web3 empowers users by utilizing technologies like blockchain and smart contracts. In this model, information is not stored on Centralised servers but on a network of computers that no single entity can control or censor.
In simple terms, to answer the question “What is Web3?”, it can be described as a transformation that gives control of data, digital assets, and even online identity back to users instead of corporations.

How Does Web3 Work?
Here’s how Web3 operates:
- Blockchain: The backbone of Web3, blockchain creates a distributed, immutable ledger that allows for data storage and transfer without intermediaries. For example, financial transactions in Web3 are carried out through Decentralised networks like Ethereum, rather than banks.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): NFTs prove digital ownership of unique assets (such as artwork or in-game items) in Web3. NFTs are recorded on the blockchain, making them nearly impossible to counterfeit or duplicate.
- Decentralised Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): In Web3, organizations are run as DAOs, where members participate directly in decision-making using governance tokens. This model replaces the hierarchical structure of traditional companies.
If you’re still wondering “What is Web3 and how does it relate to cryptocurrency?”, the answer lies in how Decentralised networks are valued. Many Web3 protocols have their own native tokens (like Ethereum or Filecoin), which serve both as network fuel and governance tools.
| According to CoinDesk, Web 3.0 uses cryptocurrencies for online purchases and money transfers, eliminating the need for banks and traditional payment systems. |
The Evolution of the Internet from Web 1.0 to Web 3.0
Since its inception in the late 20th century, the internet has undergone remarkable transformations. The question “What is Web 3?” leads us to explore the evolution of the internet from Web 1.0 to Web 3.0. This journey reflects big changes in how users interact with the digital world.
| Era | Timeframe | Interaction | Example |
| Web 1.0 | 1990–2004 | Read-Only (Static) | Yahoo Directory, Personal HTML pages |
| Web 2.0 | 2004–Present | Read-Write (Interactive) | Facebook, YouTube, Twitter |
| Web 3.0 | 2014–Future | Read-Write-Own (Decentralised) | Ethereum, Uniswap, Brave |
Web 1.0: The Era of Static Information (1990-2004)
The first generation of the internet, Web 1.0, was defined by simple HTML pages and one-way communication. During this period, users were primarily content consumers, with no ability to interact or generate content. Websites like Yahoo or early directories were prime examples of this era. The key feature of Web 1.0 was its focus on delivering information without user participation. The internet, at the time, functioned more like a “digital book.”
Web 2.0: The Revolution of Interaction and Participation (2004-present)
With the emergence of Web 2.0 in the early 2000s, the internet became an interactive, user-centered space. Known as the “read-write web,” this period saw the rise of social networks like Facebook and YouTube. Technologies such as JavaScript, AJAX, and HTML5 enabled the creation of dynamic, interactive content. Users became not only consumers but also producers of content. However, Web 2.0 remained under the control of large corporations, which collected and managed user data.
Web 3.0: The Birth of the Decentralised Internet (2014-present)
Introduced in 2014 by Gavin Wood, Web 3.0 is the vision for a Decentralised internet. Using blockchain technology, Web 3.0 gives control of data back to the users, eliminating intermediaries. Decentralised applications (dApps) and smart contracts strengthen this ecosystem, offering a transparent and secure experience. Web 3.0 is redefining the internet as a space where users are at the center.
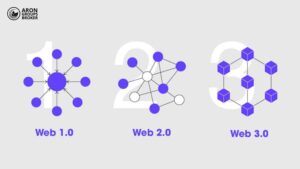
Why Was This Transformation Necessary?
While Web 2.0 brought many benefits, it also introduced problems such as data misuse, censorship, and economic monopolies. Web 3.0 addresses these challenges by returning control to the users. Today, projects like Ethereum and IPFS are laying the technical foundations of Web 3.0, demonstrating how the future internet can be freer and fairer.
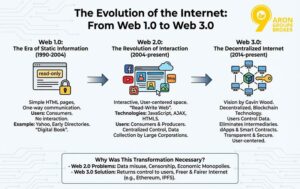
The Difference Between Web 3 and Web 2
To understand what Web3 is, it is essential to compare it with Web2. Web2 and Web3 differ significantly in terms of data management, digital ownership, and privacy, which dramatically change our internet experience.
In Web2, large companies like Google and Facebook collect and control user data. When you use platforms like Instagram or YouTube, your information is stored on their servers, often used for advertising purposes. This means you have little control over your data, and your privacy may be compromised. For instance, incidents like data breaches have shown how vulnerable Web2 can be.
On the other hand, Web3 tells a different story. Using blockchain technology, Web3 stores data on a Decentralised network. This means you own your data and digital assets. For example, with digital wallets or NFTs, you can choose with whom to share your information.
Furthermore, Web3 provides enhanced security. Since data is encrypted and not stored on Centralised servers, it is much harder to hack. Web3 also increases transparency, as all transactions are traceable and immutable. These differences make Web3 an attractive option for the future of the internet.
Here’s a summary table to help understand the differences better:
| Feature | Web 2 | Web 3 |
| Data Control | Controlled by large companies (Centralised) | Controlled by users (Decentralised) |
| Digital Ownership | Limited. Data belongs to companies | Full ownership. Users own their data |
| Privacy | Vulnerable. Risk of data breaches | Safer. Encrypted data |
| Transparency | Low. Dependent on companies | High. Transactions are traceable and immutable |
Applications of Web 3 in the Digital World
Web 3 is not just an abstract concept; it is the foundation for practical transformations across various digital sectors. From the virtual world to financial systems, this technology has enabled applications that were previously unimaginable. Let’s explore some of the most important uses of Web 3 in the digital landscape:
DeFi: Banking Without Banks
Decentralised Finance (DeFi) is one of the most revolutionary applications of Web 3. In the DeFi ecosystem, traditional financial services such as lending, insurance, and currency exchange are carried out without the need for banks or Centralised institutions. Protocols like Uniswap (a Decentralised exchange) and Aave (a lending platform) use smart contracts to enable direct user interaction. In DeFi, you connect directly to the network with your cryptocurrency wallet, eliminating the need for identity verification and reducing transaction fees.
NFTs: A Revolution in Digital Ownership
Web 3’s NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) have redefined the concept of ownership in the digital space. These tokens, registered on the blockchain, allow the buying and selling of unique assets like artwork, music, and even tweets. For example, artists can publish their work as NFTs and directly profit from its sale without needing physical galleries. Projects like CryptoPunks and Bored Ape Yacht Club have demonstrated how NFTs can evolve into billion-dollar markets.
Decentralised Applications (dApps): The Future of Software
dApps (Decentralised applications) are the core of the Web 3 ecosystem. These applications run on blockchain networks and have no central server. For instance, Brave, a Web 3 browser, blocks intrusive ads and rewards users with BAT tokens, showcasing how dApps can offer both privacy and incentivization. Another example is Audius, a Decentralised music streaming service that connects artists directly to listeners, sharing advertising revenue between them.
These Web3 Examples show how Web 3 is not just about theory but is actively transforming the way we interact with technology, providing more control, security, and ownership for users across various digital sectors.
Key Technologies of Web 3
Web 3 creates a Decentralised and user-centric experience through innovative technologies such as blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), and digital tokens. These technologies collectively shape the Web 3 ecosystem, transforming the way we interact with the digital world.
- Blockchain: The Heart of Web 3
- Blockchain is the core of Web 3, enabling data storage on a secure and Decentralised network.
- It ensures data integrity and transparency, and removes the need for Centralised control, forming the foundation for Decentralised applications.
- Smart Contracts: Automating Trust
- Smart contracts are self-executing applications on the blockchain that carry out transactions without intermediaries.
- Platforms like Ethereum use smart contracts to ensure transparency, reliability, and cost reduction, automatically executing the agreed terms of a contract.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Semantic Web
- AI helps Web 3 process data intelligently, providing personalized experiences such as content recommendations on Decentralised platforms.
- The Semantic Web structures information to allow machines to better understand and interpret web content, enhancing automation and data interoperability.
- NFTs: A New Era of Digital Ownership
- NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) are unique digital assets representing ownership of items such as artwork, in-game items, or even virtual real estate on the blockchain.
- NFTs enable users to directly control and trade their digital assets, fostering new ways to monetize and prove ownership in the digital economy.
- According to DappRadar, the NFT market is expected to experience significant growth by 2024.
These Web3 examples illustrate how Web3 leverages these cutting-edge technologies to empower users, provide greater control, and revolutionize the way we interact with the digital world.

How to Get Started with Web 3
Entering the world of Web 3 may seem complex at first, but with a few simple steps, you can easily connect to this transformative ecosystem. Whether you’re curious about Whether you want to know what Web3 is or understand Web 3.0’s meaning, these practical steps will guide you through your journey into Web 3.
Here are the essential steps to start your experience with Web 3:
- Install a Cryptocurrency Wallet
- Use Web 3 Browsers
- Participate in DAO Projects
1. Install a Cryptocurrency Wallet
The first step to entering Web 3 is setting up a cryptocurrency wallet. Wallets like MetaMask and Trust Wallet act as your entry point to the Decentralised internet. These wallets not only store Web3 crypto assets like Ethereum or Bitcoin, but also connect you to Decentralised applications (dApps), allow you to purchase NFTs, and help you engage in DAO projects. Once set up, you’ll receive a private key, which is crucial to keeping your digital assets secure, treat it like a bank password.

2. Use Web 3 Browsers
Traditional browsers like Chrome or Firefox are not optimized for interacting with Web 3. To truly experience Web 3, use browsers specifically built for this new ecosystem, such as Brave or Opera Web3. These browsers support Decentralised internet protocols, block annoying ads by default, and reward users with tokens. For example, Brave rewards users with BAT tokens for viewing non-intrusive ads, which is a key feature of Web 3’s new economic model.
3. Participate in DAO Projects
DAO (Decentralised Autonomous Organizations) projects are essential to the functioning of Web 3. By buying governance tokens from DAOs (such as Uniswap or Aave), you gain the ability to vote on important decisions within the organization. Some DAOs even reward active members. Platforms like Snapshot or DAOhaus provide lists of active DAO projects, allowing you to join based on your interests. This is an example of Web3 that demonstrates the shift toward Decentralised, user-driven decision-making.
Once your wallet and browser are set up, you can connect to Decentralised applications (dApps). For example, explore platforms like OpenSea (for NFTs), Uniswap (a Decentralised exchange), or Decentraland (a metaverse project). These platforms allow you to connect your wallet seamlessly through a “Connect Wallet” button.
By following these steps, you’ll not only understand how to invest in Web3, but you’ll also become an active participant in the Web 3 ecosystem. From owning digital assets to contributing to Decentralised governance, you’ll be part of the revolution that is shaping the future of the Decentralised internet.

Smart Contracts and Web 3
Smart contracts are self-executing codes that run on the blockchain and manage transactions without intermediaries. This technology is fundamental to Web 3 and is the backbone of Decentralised financial systems such as DeFi. For example, platforms like Aave automate the lending process, allowing users to lock their assets in liquidity pools, approve borrowers, and calculate interest rates automatically, all without the involvement of banks or Centralised entities.
The main advantages of smart contracts in Web 3 include:
- Cost reduction
- Transparency
- Security
These contracts are used not only in DeFi but also in areas like NFT management and DAO governance. For instance, an artist can use a smart contract to automatically receive royalties from the sale of their artwork. This technology is driving the Decentralised economy of Web 3, enabling business models that were previously unimaginable.

Challenges and Opportunities in Web 3
Web 3 is a transformative technology, but it faces both challenges and opportunities that will influence its development. Understanding these hurdles and potentials helps us better grasp Web 3’s role in the digital future. If you’re wondering what the challenges and opportunities of Web 3 are, keep reading.
Technical Challenges
One of the primary barriers to Web 3 is technical scalability. For example, the Ethereum network occasionally faces high transaction fees and slower speeds due to the limitations of blockchain technology. Furthermore, using Decentralised applications (dApps) can be difficult for average users, as it requires technical expertise and a digital wallet. These challenges slow down the widespread adoption of Web 3.
Legal Challenges
Legal barriers also pose significant concerns. Many countries have unclear or restrictive regulations regarding cryptocurrencies and smart contracts. For example, strict regulatory frameworks in some regions may hinder innovation in the Decentralised economy. Additionally, security concerns, such as attacks on smart contracts, threaten user trust in Web 3.
Opportunities
Despite these challenges, Web 3 offers vast opportunities. The Decentralised economy empowers users to earn from their data and digital assets, such as selling NFTs or engaging in DeFi platforms. From a social perspective, Web 3 promotes freer digital communities by enhancing privacy and reducing censorship. According to a DappRadar report (2024), the growing transaction volumes in DeFi and NFT markets highlight the immense economic potential of Web 3.
In conclusion, while Web 3 faces both technical and legal challenges, its potential to reshape digital economies and empower individuals is profound, opening up new opportunities for privacy, ownership, and Decentralised governance.
Examples of Web 3 Projects
To gain a deeper understanding of Web 3, examining real-world projects is essential. These projects not only bring Web 3 concepts to life but also showcase how Web3 crypto works and its role in Decentralised networks.
- Ethereum: The Pioneer of Smart Contracts
- Ethereum is one of the leading Web 3 projects and the second-largest cryptocurrency platform after Bitcoin.
- Introduced smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts that automate transactions without intermediaries.
- Enables developers to create dApps and Decentralised protocols such as Uniswap (a Decentralised exchange) and Aave (a lending platform).
- The cryptocurrency Ether (ETH) is an example of Web3 crypto and is used both as network fuel (to pay transaction fees) and as a digital asset for investment and trading.
- Filecoin: A Revolution in Cloud Storage
- Filecoin offers a Decentralised alternative to Centralised cloud storage services like Google Drive or Dropbox.
- Uses unused storage space from users worldwide to create a secure and distributed network.
- Users can rent out their storage space and earn FIL tokens in return.
- This model reduces costs and guarantees privacy through advanced encryption.
- Filecoin is a key example of Web3 crypto, where value is generated from user participation in the network.
These Web 3 examples demonstrate how Web3 crypto and Decentralised applications are reshaping the digital landscape, creating more secure, transparent, and user-centric ecosystems.

Best Web 3 Projects in Cryptocurrency for 2025
In 2025, the Web 3 ecosystem will witness the emergence of projects that not only define the concept of “What is Web3?” but also shape the future of the Decentralised internet. Here are some of the leading Web 3 projects in the cryptocurrency space that have the potential for significant growth in the coming years:
- Solana
- Solana is one of the rising stars of Web 3. This blockchain offers high speed and low costs, making it an ideal platform for Decentralised applications (dApps) such as DeFi and NFTs.
| According to CoinMarketCap reports in 2024, Solana will continue to be a leader in 2025 due to the growth of its ecosystem and increasing number of projects. |
- Chainlink
- Chainlink plays a vital role by connecting real-world data to smart contracts, which are essential for DeFi platforms.
- With the growing demand for secure data, especially in projects that rely on digital trust, Chainlink has significant growth potential in 2025.
- Polkadot
- Polkadot connects different blockchains, enabling interoperability between networks. This is crucial for the future of Web 3.
- According to gov.capital in 2024, the expansion of Polkadot’s parachain networks makes it one of the top Web 3 projects for 2025. By focusing on innovation and user-centric designs, Polkadot is helping shape the future of the Decentralised Internet.
These Web 3 projects demonstrate how Web3 crypto and blockchain technologies are pushing the boundaries of Decentralised systems, creating new opportunities for the future of the internet.

Web 3 Applications
How does Web 3 manifest through applications? The answer lies in Decentralised applications (dApps). These applications, running on the blockchain, take control of data and operations away from Centralised companies and return them to the users. Two prominent examples of dApps are Decentralised exchanges and Decentralised social platforms, which have transformed the way we interact with the internet. Here are some exciting examples of these applications:
- Uniswap
- Uniswap is one of the most well-known Decentralised applications (dApps), acting as a Decentralised exchange (DEX).
- With Uniswap, you can trade cryptocurrencies directly from your digital wallet without relying on traditional exchanges.
Uniswap saw over $18 billion in trading volume during the first week of 2025. This dApp uses smart contracts to make transactions fast, transparent, and secure.
- Audius
- Audius is a Decentralised social platform for music streaming, allowing artists to share their works directly with their audience.
- By utilizing blockchain technology, Audius eliminates intermediaries, giving artists greater control over their income and content.
- The platform reduces censorship and offers a user-centric experience.
These applications illustrate how Web 3 is breaking the monopolies of large companies. dApps reduce costs, increase transparency, and return digital ownership to users. From buying and selling NFTs to participating in DAOs, dApps are shaping a future where users, not platforms, are the final decision-makers.

Best Web 3 Browsers
To fully engage with the Web 3 ecosystem, it is essential to use the right tools, such as Web 3 browsers. These browsers are specifically designed for the Decentralised internet, enabling users to interact with dApps and manage Web3 crypto seamlessly. Let’s take a look at some of the best Web 3 browsers and extensions that are leading the way in Web 3.0 meaning.
Brave Browser: A Top Choice for Web 3 Users
Brave is one of the most popular choices for users looking to explore the benefits of Web3, such as ownership and privacy. By blocking ads and trackers, Brave enhances privacy and supports blockchain protocols. With high-speed browsing and the ability to interact directly with Decentralised applications (dApps), Brave offers an ideal experience for anyone engaging with Web 3. Users can also manage their Web3 crypto assets using the built-in cryptocurrency wallet, making Brave an all-in-one tool for Web 3 enthusiasts.
MetaMask Extension: A Key Tool for Web 3
The MetaMask extension is an essential tool for anyone looking to dive into the Web 3 ecosystem. It allows users to manage their digital wallets, trade cryptocurrencies, and easily connect to dApps. MetaMask simplifies the process of entering the Decentralised internet, providing a user-friendly interface that makes Web 3 more accessible. For those wondering how to invest in Web3, MetaMask offers a seamless gateway to explore Decentralised finance (DeFi), NFTs, and more.
These Web3 examples show how Web 3 browsers and extensions are crucial for accessing the Decentralised internet, ensuring that users can experience Web 3’s full potential. By offering both privacy and ease of use, these tools empower users to take control of their digital identities and assets.
How to Earn Money Through Web 3
How can you earn money through Web 3? The answer lies in methods like staking, selling NFTs, and participating in Decentralised governance (DAO). Let’s explore these ways of earning within the Web 3 ecosystem.
Staking: Earning Passive Income
Staking is the process of locking up digital assets in Proof of Stake (PoS) networks to help secure the network while earning rewards. For example, by staking Ethereum 2.0 or Solana (SOL), you can earn annual returns of up to 10%. This method not only provides passive income but also contributes to strengthening the Decentralised economy of Web 3.
Selling NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens)
Selling NFTs is another popular way to earn money through Web 3. NFTs are unique digital assets such as artwork, in-game items, or collectibles. By creating and selling NFTs on platforms like OpenSea, you can monetize your digital creations.
| According to Solulab.com, the NFT market continued to thrive in 2024, showing the growing opportunity for creators to profit from Web 3. |
Decentralised Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
DAOs allow users to earn by participating in governance decisions. For example, in Uniswap Governance, UNI token holders can vote on protocol changes and earn rewards in return. Some DAOs, such as MakerDAO, even pay active members a salary. This model combines Decentralised governance with financial opportunities, enabling users to earn while participating in decision-making processes that shape the future of Web 3.
These methods illustrate how Web 3 opens new avenues for earning income while participating in the Decentralised internet. Whether through staking, creating and selling NFTs, or engaging in DAO governance, Web 3 provides diverse and innovative ways to profit in the digital economy.

The Future of Web 3
What does the future of Web 3 look like, and how will it shape the internet and digital life? The answer lies in the integration of Decentralised technologies with innovative concepts like the metaverse. Web 3, as the foundation of this transformation, will return ownership of digital assets, identity, and social interactions to users, paving the way for a more open and fair world.
The Integration of Web 3 with the Metaverse
The metaverse, as an advanced version of virtual reality, requires infrastructure where users have full ownership of their assets. This is where Web 3 comes into play, with technologies like NFTs and blockchain. In a Web 3-based metaverse, virtual lands, game items, and even avatar clothing are registered as non-fungible tokens, allowing users to buy and sell them in Decentralised markets. Projects like Decentraland and The Sandbox are early examples of this integration, showing how the future of the internet will unfold.

Impact on Privacy and the Economy
By replacing Centralised systems with Decentralised networks, Web 3 strengthens user privacy. In this model, data is stored on the blockchain, not on company servers, and access to this data is only granted through users’ private keys. Economically, Web 3 offers direct earning opportunities through NFT sales, participation in DAOs, or providing services in the metaverse.
While Web 3 promises a bright future, challenges such as network scalability and regulatory frameworks remain. However, advancements in technologies like artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT) could accelerate these developments. Ultimately, Web 3 will redefine not only the future of the internet but also how humans interact with technology, art, and even their own identity.
Conclusion
Web 3 is not just a new version of the internet; it is an effort to return the internet to the people. However, the real opportunities of Web 3 lie not in the technology itself, but in the minds of those who understand it early and take action today to help shape the future. By embracing Web 3 now, individuals and businesses can be at the forefront of this revolutionary change, creating a more Decentralised, user-centric digital world.
































