In financial markets that are constantly influenced by economic and political forces, economic reports play a crucial role in shaping investors’ decisions. Among the most important of these reports is the U.S. Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP) report, published monthly by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). This report serves as a key indicator for assessing the health of the labor market and overall economic growth in the United States. Its influence extends far beyond employment; it directly affects both the foreign exchange (forex) and stock markets.
In this article, we’ll take an in-depth look at the NFP report, examine its broader effects on global markets, and explore various trading strategies that investors use based on its outcomes.
Definition of the Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP) Report
The Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP) report is one of the most significant economic indicators in the United States. It measures the change in the number of employed people during the previous month, excluding workers in the agricultural sector. The report is compiled and released each month by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, drawing from employment data submitted by businesses and government agencies across the country.
The NFP report includes three key components:
- Job creation data: the total number of new jobs added.
- Unemployment rate: the percentage of people actively seeking work but currently unemployed.
- Average hourly earnings: a measure of wage growth and consumer purchasing power.
Each of these metrics provides valuable insights into the economy’s overall performance and plays a critical role in shaping monetary policy decisions, particularly those made by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The unemployment rate reflects the number of job seekers unable to find employment, while the change in average hourly earnings indicates shifts in labor costs and inflationary pressure, both vital for gauging the strength of consumer demand.
Due to seasonal and weather-related fluctuations in agricultural employment, the NFP report focuses on non-agricultural sectors such as industry, trade, and services. This approach provides a more stable and representative picture of the U.S. economy’s underlying trends. Consequently, the NFP has become a leading economic indicator that analysts, currency traders, and institutional investors rely on to forecast future economic developments and plan their investment strategies.
As a core economic report, NFP data has a direct and often immediate impact on financial markets, especially the forex and equity markets. For this reason, financial analysts closely monitor its release to evaluate the strength of the U.S. economy and to adjust their investment and trading strategies accordingly.

Methodology and Data Collection for the NFP Report
The Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP) report is compiled using two primary surveys conducted by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS):
- Household Survey (Current Population Survey):
This survey provides insights into the unemployment rate and the broader economic condition of households, capturing data on labor force participation, demographic employment trends, and job-seeking activity. - Establishment Survey (Current Employment Statistics Survey):
This survey measures changes in the number of paid employees across various non-agricultural industries, such as manufacturing, services, and trade. The establishment survey serves as the core dataset for the NFP report and is collected monthly from thousands of employers nationwide.
The results are typically released on the first Friday of each month, making it one of the most anticipated data points for financial markets. For traders, the NFP report represents a key opportunity to anticipate short-term market movements and adjust trading strategies accordingly.
The Impact of the NFP Report on Financial Markets
The NFP report exerts a profound influence on global financial markets, including foreign exchange (forex), equities, and bond markets. Because it offers a comprehensive snapshot of U.S. economic health, it directly shapes investor sentiment and market expectations about future monetary policy and growth prospects.
Impact on the Foreign Exchange (Forex) Market
Since the U.S. dollar (USD) serves as the base or quote currency in the majority of global forex transactions, NFP data has an immediate and significant effect on major currency pairs.
- When the report signals strong job growth and rising wages, it typically boosts the dollar’s value against other currencies, reflecting expectations of a stronger economy and potential interest rate hikes by the Federal Reserve.
- Conversely, weaker-than-expected employment data can lead to dollar depreciation, as investors anticipate looser monetary policy or slower growth.
The most affected pairs are usually EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and GBP/USD, where volatility tends to spike in the minutes following the report’s release.
Impact on the Stock Market
In the equity market, the NFP report serves as a barometer for domestic economic expansion and consumer demand.
- Positive NFP results, such as increasing employment and higher wages, tend to strengthen stock indices, particularly for companies focused on the domestic market, as stronger labor conditions often lead to higher consumer spending and corporate earnings.
- However, in inflationary environments, robust job growth may signal persistent inflationary pressure. This can prompt the Federal Reserve to raise interest rates, a move that typically weighs on stock valuations due to higher borrowing costs and reduced future cash flow value.
Thus, investors must interpret NFP data within the broader macroeconomic context, considering factors like inflation trends, wage growth, and central bank policy.
Impact on Bonds and Interest Rates
The NFP report is one of the primary determinants of interest rate expectations. The Federal Reserve closely monitors this data to guide its monetary policy decisions.
- Strong NFP figures, indicating rising employment and wage levels, suggest economic expansion, increasing the likelihood of rate hikes to curb potential inflation.
- Higher interest rates generally strengthen the U.S. dollar while reducing the appeal of U.S. Treasury bonds, as yields rise and existing bond prices decline.
In essence, the NFP acts as a leading indicator for monetary tightening or easing cycles, influencing not only short-term trading but also long-term investment positioning across asset classes.
Trading Strategies Based on the NFP Report
The Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP) release is one of the most market-moving data points in macroeconomics. It often triggers rapid swings in currencies and equities, so professionals approach it with clear playbooks and strict risk control. Strategies generally fall into two groups: those set before the data drops and those taken after the numbers hit the tape.
Pre-Release Trading Strategies
Before the report, traders use forecasts and leading indicators to frame expectations.
If consensus points to strong job growth, they may go long the U.S. dollar ahead of time, expecting the currency to strengthen once the data confirm it. This approach demands precise analysis and tight position sizing.
Forecasting and Market Sentiment Analysis
Market participants compare economists’ estimates, prior NFP prints, and data such as ADP employment or initial jobless claims to infer direction. Anticipating a positive surprise, they might accumulate dollars; expecting weakness, they might sell.
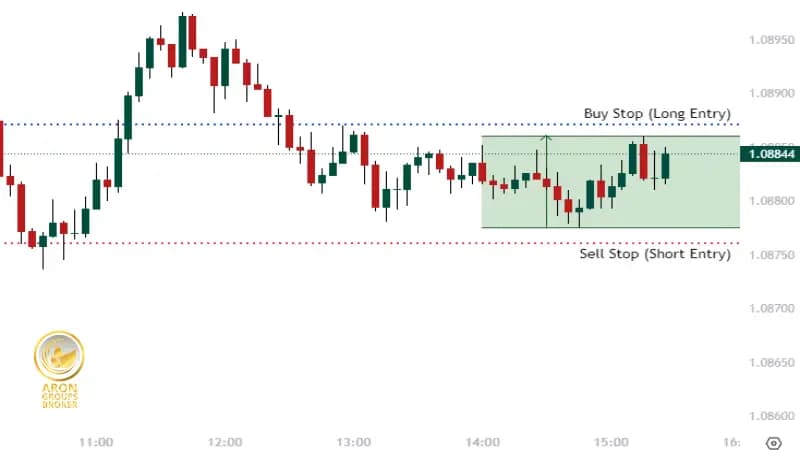
Range Trading Strategy
Roughly 10-15 minutes before the release, some traders mark the session’s short-term high and low and place a buy-stop just above the range and a sell-stop just below. Whichever side breaks first becomes active as volatility explodes. Immediate stop-loss orders cap downside if the breakout fails.
Position Sizing and Risk Control
Because pre-release volatility can be chaotic, professionals typically cut position size and ensure every trade has a defined exit. Stop-loss discipline keeps a single event from damaging total capital.
Post-Release Trading Strategies
Once the figures are out, speed and interpretation matter. Traders compare the actual data with expectations and watch the first price reaction.
Fade Trading (Reversal Strategy)
Markets often overreact. In a fade setup, traders wait for the initial surge, then trade against it once momentum stalls. For example, if USD/JPY spikes higher on a blowout jobs number, a contrarian may short the pair, anticipating a short-term pullback as profit-taking sets in.
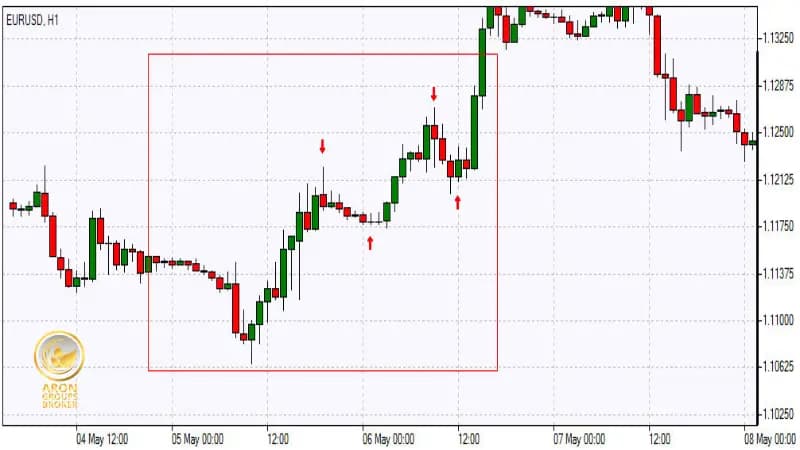
Momentum Trading Strategy
If the data deviates sharply from forecasts and the move holds, traders ride the wave instead of fading it. A far-stronger-than-expected report can ignite a sustained dollar rally; buying dips during that impulse follows the momentum logic.
Swing Trading Strategy
Beyond intraday noise, the NFP often signals a broader direction for weeks ahead. A sequence of strong reports can underpin a month-long uptrend in the dollar or equities, encouraging swing traders to hold positions over multiple sessions rather than chasing every tick.
Risk Management Tools in NFP Trading
Risk management tools used in NFP (Non-Farm Payrolls) trading include Stop Loss and Take Profit orders, OCO (One Cancels the Other) orders, and position size control.
These tools help traders manage the high volatility that follows the NFP release and limit potential losses. The following sections explain each of these tools in more detail.
Stop Loss & Take Profit Orders
Using Stop Loss and Take Profit orders is one of the essential tools for risk management.
By setting a predetermined exit level, such as a Take Profit target equal to 2.5 times the Stop Loss, traders can secure their profits against market volatility.
For example, if a Stop Loss is set at 4 pips, the corresponding Take Profit target could be 10 pips, maintaining a healthy risk-to-reward balance.
OCO (One Cancels the Other) Orders
An OCO order consists of two pending orders in opposite directions. When one order is executed, the other is automatically canceled.
This setup is particularly useful around major economic announcements such as the NFP, where the market can move sharply up or down within seconds.
Position Sizing and Leverage Reduction
During periods of extreme volatility, such as NFP releases, reducing trade volume and using lower leverage is a prudent way to manage exposure.
High leverage magnifies both gains and losses, so scaling down positions helps protect capital when prices move unpredictably.
The Relationship Between NFP and Interest Rates
According to an article regarding the NFP (Non-Farm Payrolls) published on Investing.com, the NFP report is a key indicator for the Federal Reserve’s interest rate decisions, as it reflects the health of the labor market. When the NFP indicates strong job growth and rising wages, the Federal Reserve typically raises interest rates to control inflation. Conversely, if the NFP indicates weakening employment, the Federal Reserve may lower interest rates to stimulate the economy.
These interest rate shifts directly impact financial markets, particularly the value of the US dollar, creating profitable opportunities for traders.
The Psychological Impact of NFP on the Market
The release of the NFP report triggers significant shifts in market sentiment. In the run-up to the report, traders often wait with anxiety and uncertainty, as any deviation from expectations can trigger significant market volatility.
Strong NFP results boost market confidence, leading investors to move into risk-on assets such as equities and higher-risk currencies. Conversely, weak results drive investors toward safe-haven assets like gold and bonds.
Analyzing NFP Data to Forecast Market Movements
Professional traders analyze various components of the NFP report, including the headline job creation number, the unemployment rate, and wage growth (often reported as Average Hourly Earnings) to gain insights into the health of the US economy and forecast potential market direction.
Changes in these data points are particularly instrumental in identifying future economic trends. If the NFP indicates strong job and wage growth, it tends to boost the value of the dollar and major stock indices. Conversely, a decline in these metrics may lead to a weakening dollar and an appreciation in safe-haven assets.
How NFP Differs from Other Employment Indicators
The NFP (Non-Farm Payrolls) is a primary employment indicator, but it differs from other metrics such as the unemployment rate and jobless claims. The unemployment rate measures the percentage of the workforce actively seeking employment, while jobless claims (specifically, Initial Jobless Claims) track the number of individuals filing for unemployment benefits for the first time.
The NFP, however, focuses specifically on the number of jobs added or lost in non-agricultural sectors, providing a more precise picture of the employment landscape.
The Impact of NFP on Forex and Stocks
According to an article on DayTrading, the NFP report is highly significant due to its widespread impact on the value of the US dollar and stock indices. When the NFP indicates strong job and wage growth, it reinforces the likelihood of an interest rate hike by the Federal Reserve, which in turn boosts the dollar’s value. Consequently, major US stock indices and other currencies traded against the dollar are affected.
Conversely, a weak NFP report typically leads to a depreciation in the dollar and a rally in safe-haven assets such as gold. These ripple effects help traders adjust their strategies based on NFP forecasts and the subsequent market reaction.
Example of Market Volatility Following an NFP Report
In August 2021, the US NFP report showed that only 235,000 new jobs had been created in the US economy. This figure was significantly below the market consensus (or “market expectations”), which had anticipated around 750,000 new jobs. This weak reading surprised the market, signaling a slowdown in US economic growth. The primary reason for the low job creation that month was the resurgence of the COVID-19 pandemic and its impact on service sectors, particularly tourism, food services, and entertainment, which continued to face significant challenges.
- Market Reaction: Immediately following the report’s release, the value of the US dollar declined. Monetary policy expectations drove this; investors anticipated that the weakness in the labor market would cause the Federal Reserve to hold off on raising interest rates. A more accommodative (or “dovish”) policy stance and delayed rate hikes tend to weaken the US dollar against other currencies.
- Impact on Gold: The dollar’s depreciation prompted investors to move toward safe-haven assets like gold. Gold, as a safe haven, sees increased demand during times of economic uncertainty, as its value is less dependent on currency fluctuations. As a result, the price of gold rose rapidly, reaching its highest level for that month.
This event highlighted just how sensitive markets are to the NFP report and its underlying data, and how expectations regarding Federal Reserve monetary policy can create sharp volatility across various markets.
Conclusion
The NFP report, as a crucial economic indicator, plays a key role in setting the direction for financial markets. By carefully analyzing this report, traders can refine their trading strategies and capitalize on profitable opportunities. Understanding the report’s psychological impact and its intrinsic link to monetary policy allows investors to make more informed decisions and improve their trading performance through better risk management.































