Portfolio diversification reduces investment risk by spreading capital across various assets, rather than relying on a single market or instrument. This approach is a core principle of sound portfolio management and a key reason why portfolio diversification is essential for long-term investors.
In the following sections, we explore the benefits of portfolio diversification and introduce practical portfolio diversification strategies you can apply across stocks, crypto, and multi-asset portfolios.

- Portfolio diversification reduces overall investment risk by combining different types of assets within a single portfolio.
- It is achieved by investing across multiple asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, cryptocurrencies, while diversifying within each class.
- Diversification of a portfolio can also be improved by spreading investments across different countries, industries, company sizes, and investment time horizons.
- The quality of investment portfolio diversification is typically measured by analysing the correlation between assets. Lower correlation leads to better risk control.
- Investors can diversify their portfolios either by selecting individual assets themselves or by investing through diversified funds such as ETFs or mutual funds.
What Is Portfolio Diversification?
According to Investopedia, portfolio diversification is a risk management strategy. It reduces reliance on a single asset or risk factor. This is achieved by combining different assets and investment instruments within one portfolio.
The purpose of diversification of a portfolio is to lower individual investment risk while improving long-term return stability. In short, the benefits of portfolio diversification materialise only when assets react differently, or even inversely, to changing market conditions.

Pro Tip:
The “magic number” in Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT) suggests that holding about 20–30 uncorrelated stocks captures most of the reduction in unsystematic risk (optimal diversification), while adding more stocks beyond that point increases complexity and costs without significantly lowering risk.
Why Is Portfolio Diversification Essential for Risk Reduction?
Portfolio diversification is a core principle of capital management because it prevents investment risk from being concentrated in a single asset or industry. In a well-structured diversification portfolio, weak performance in one area can be offset by stronger performance in other areas.
This approach is especially effective in reducing unsystematic risk, as it limits exposure to risks specific to a single company, sector, or region. As a result, investment portfolio diversification makes portfolios more resilient to unexpected events.
Read more: What are systematic and unsystematic risks?
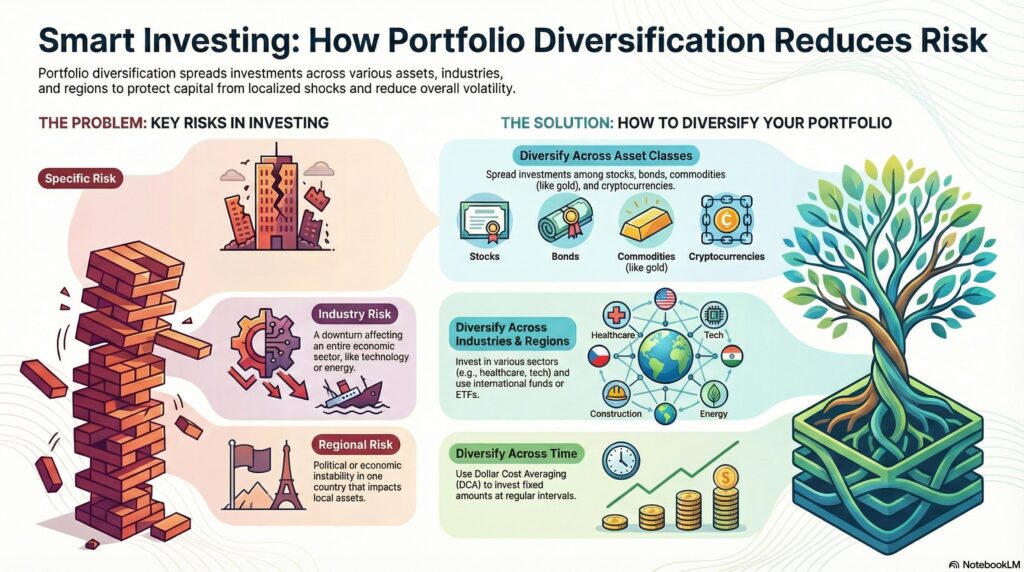
Types of Risk Reduced Through Diversification
Effective portfolio diversification strategies can help mitigate several types of risk, including:
- Specific risk: Company-level issues such as poor management decisions or declining sales.
- Industry risk: Economic downturns affecting a specific sector, such as the automotive or energy industry.
- Regional risk: Political or economic changes in a specific country that impact local assets.
Q: Does portfolio diversification protect investors during systemic financial crises?
A: During systemic financial crises, asset correlations often increase, which reduces the short-term effectiveness of portfolio diversification in lowering volatility. However, this does not make diversification ineffective. Its primary role in such periods is to limit permanent capital loss and preserve the portfolio’s ability to recover after the crisis.
Because assets differ in risk structure, cash flow stability, and liquidity, they experience varying degrees of drawdown and recover at different speeds. Combining assets that respond differently to systemic shocks enhances portfolio resilience and supports long-term stability, making diversification a critical tool for risk management beyond short-term market stress.

Warning:
While portfolio diversification cannot remove systematic risk, including global economic shocks, it can significantly limit its impact on overall portfolio performance.
Correlation and Its Role in Portfolio Diversification
Correlation measures how closely the prices of two assets move in relation to each other.- High positive correlation: Two assets tend to rise and fall together, such as stocks within the same industry.
- Negative correlation: When one asset rises, the other tends to fall, as is sometimes observed between equities and gold.
Practical Example: How Diversification Affects Portfolio Performance
Consider two investors:- Investor A invests all capital in the shares of a single technology company.
- Investor B spreads capital across technology stocks, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), bonds, and gold.
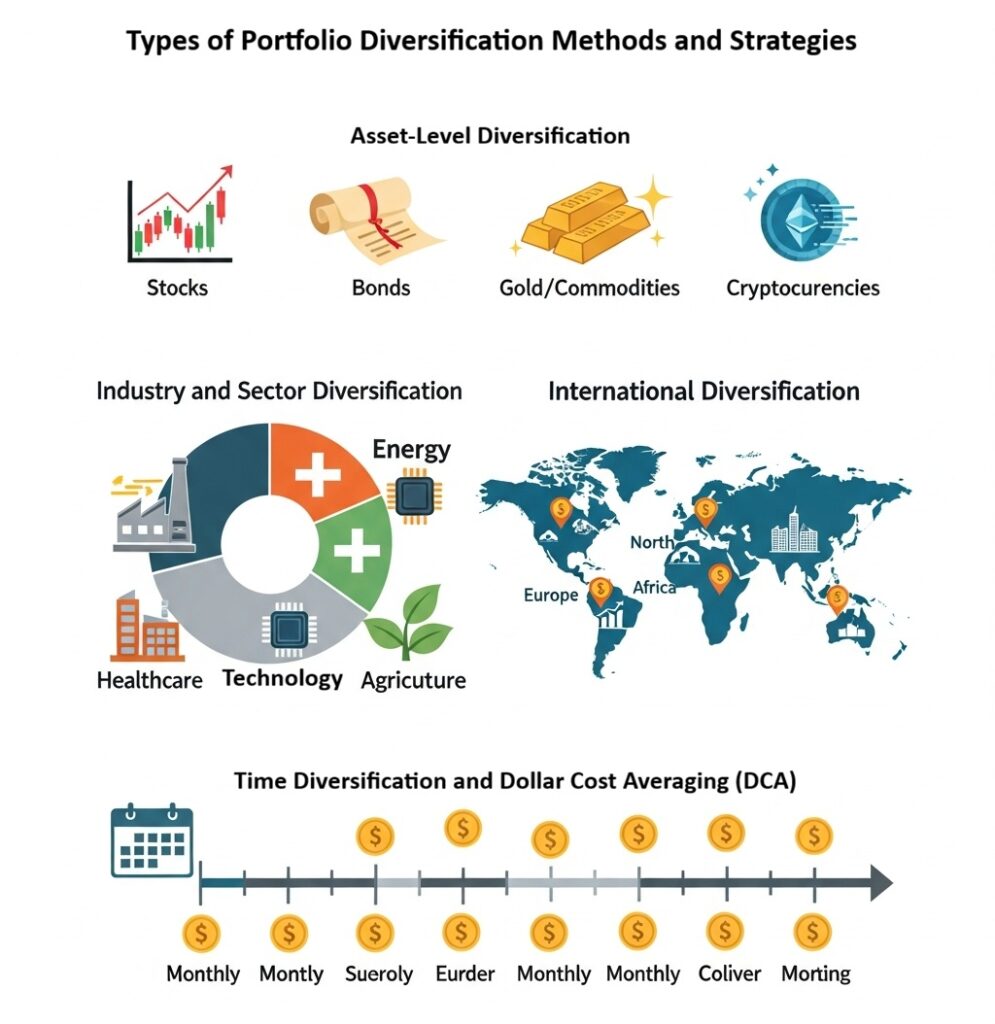
Types of Portfolio Diversification Methods and Strategies
To build a balanced and lower-risk investment portfolio, investors can apply different portfolio diversification strategies. The objective is to combine assets in a way that reduces overall volatility and delivers more stable long-term returns. There are several practical approaches to diversification of a portfolio, outlined below.Asset-Level Diversification
This method involves spreading capital across different asset classes, such as:- Stocks,
- Bonds,
- Gold and other commodities,
- Cryptocurrencies,
- Cash or bank deposits.
Industry and Sector Diversification
Investing in a single industry carries elevated risk. By allocating capital across multiple sectors, such as energy, healthcare, technology, and agriculture, the impact of a downturn in any one sector is reduced. This type of diversification portfolio is particularly effective in lowering industry-specific risk, one of the key advantages of portfolio diversification.International Diversification
Investing in foreign markets helps reduce exposure to domestic political and economic risks. This can be achieved through:- Global or regional exchange-traded funds (ETFs),
- International equity or bond funds.
Time Diversification and Dollar Cost Averaging (DCA)
With Dollar Cost Averaging (DCA), investors allocate capital gradually rather than making a single lump-sum investment. Fixed amounts are invested at regular intervals.
This strategy:
- Lowers the average purchase price over time,
- Reduces the impact of short-term market volatility,
- Supports disciplined, long-term investing.
DCA is widely used in stock portfolio diversification and crypto portfolio diversification, especially in volatile markets.
Q: Which portfolio diversification strategy is most important for reducing risk?
A: Asset-level diversification is the foundation. Without exposure to multiple asset classes, other strategies, such as sector or international diversification, have limited impact. Once this base is in place, combining it with industry, geographic, and time diversification produces the strongest risk-adjusted results.
Comparison Table: Portfolio Diversification Strategies
| Feature | Asset-Level Portfolio Diversification | Industry Portfolio Diversification | International Portfolio Diversification | Time Diversification (Dollar Cost Averaging – DCA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main purpose | Reduce risk from relying on a single asset class (e.g. stocks only) | Reduce risk from downturns in one specific industry (e.g. technology) | Reduce risk from economic and political shocks in one country | Reduce short-term price volatility and poor entry timing |
| How it works | Allocate capital across multiple asset classes | Spread investments across different sectors | Invest in foreign markets and global assets | Invest fixed amounts at regular intervals over time |
| Common instruments | Stocks, bonds, gold, cryptocurrencies, cash | Sector stocks (energy, healthcare, financials, etc.) | Global ETFs or foreign company shares | Scheduled weekly or monthly purchases |
| Risks reduced | Asset-specific risk | Industry-specific risk | Regional and political risk | Market volatility and timing risk |
| Complexity level | Medium | Medium | High (requires knowledge of global markets) | Low |
| Best suited for | Most investors seeking balanced risk | Long-term investors building resilient portfolios | Investors with larger capital seeking global exposure | Beginner and professional investors managing entry points |
Best Tools for Analysing and Optimising a Diversified Portfolio
To ensure that your portfolio diversification remains balanced and risk-efficient, using portfolio analysis and monitoring tools is essential. These tools enable investors to evaluate returns, assess risk levels, analyse asset correlations, and optimize the structure of a diversification portfolio as needed.Portfolio Analysis Software and Platforms
Platforms such as TradingView, Portfolio Visualiser, and brokerage-provided analytics tools enable investors to:- Review historical portfolio performance,
- Measure portfolio risk and volatility,
- Compare different investment scenarios.
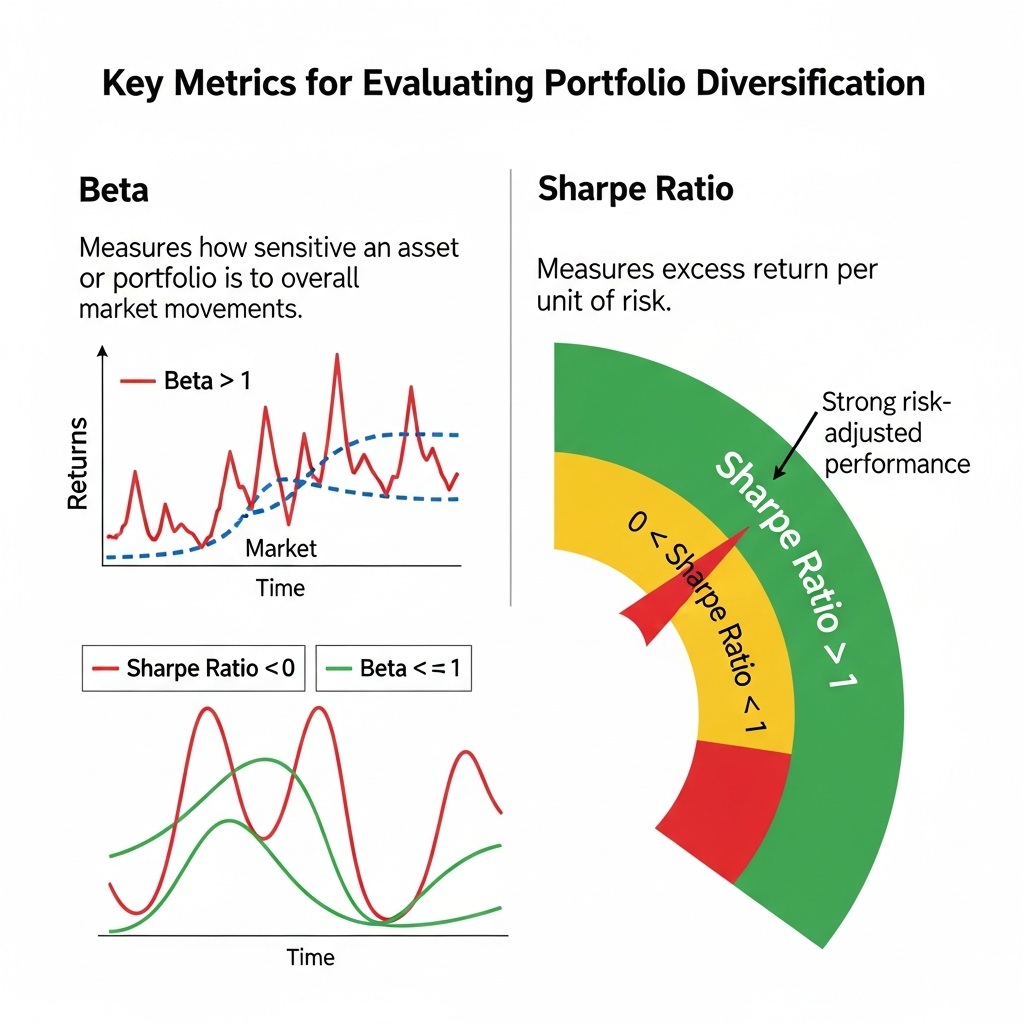
Key Metrics for Evaluating Portfolio Diversification
Certain financial metrics play a central role in assessing the effectiveness of portfolio diversification strategies:- Beta:
Measures how sensitive an asset or portfolio is to overall market movements.
- A beta below 1 indicates lower volatility than the market.
- A beta above 1 indicates higher volatility than the market.
- Sharpe Ratio:
Measures excess return per unit of risk.
- A Sharpe ratio above 1 generally signals strong risk-adjusted performance.

Key Insight:
Dynamic diversification, which is actively adjusted in response to market conditions, significantly enhances portfolio risk management.
Using these indicators together allows investors to evaluate the quality of their portfolio diversification strategy with greater precision and make more informed optimisation decisions.
The Role of Financial Advisors and Robo-Advisors in Portfolio Diversification
Human financial advisors play a crucial role in portfolio diversification by designing personalised investment strategies tailored to individual goals, risk tolerance, and current market conditions. Their value lies in their judgment, experience, and ability to adapt to changing markets. In practice, they:
- Assess personal financial objectives and risk profiles,
- Recommend optimal asset allocation across markets,
- Adjust portfolio composition to manage risk and enhance returns.
Robo-advisors complement this approach by providing systematic and data-driven portfolio management. Using algorithms and predefined rules, they help maintain investment portfolio diversification over time. Their core functions include:
- Suggesting suitable asset mixes automatically,
- Periodic portfolio rebalancing based on market movements,
- Maintaining alignment with the chosen diversification strategy.
When combined, human expertise and automated tools create a balanced investment approach. This hybrid model supports consistent optimisation, improves risk control, and keeps the diversification portfolio aligned with long-term financial goals—one of the key benefits of portfolio diversification.
Q: How should portfolio diversification be adjusted as capital grows?
A: As portfolio size increases, diversification should shift from simply adding assets to strategic risk management and optimization. Larger portfolios allow for:
- Precise asset allocation: balancing exposures across asset classes based on expected risk and correlation.
- Including alternative investments, such as real estate, private funds, commodities, and structured products, helps manage volatility and reduce drawdowns.
- Active risk control: using hedging, weighting adjustments, and volatility management to prevent concentration risks.
- Focus on net returns: considering taxes, transaction costs, and fees to preserve after-tax performance.
- Ongoing monitoring: periodically reviewing and adjusting the portfolio ensures alignment with market conditions and long-term goals.
In short, for larger portfolios, diversification serves as a tool for risk-adjusted growth, capital preservation, and volatility control, rather than simply spreading exposure across multiple assets.
Common Portfolio Diversification Mistakes
If portfolio diversification is done incorrectly, it can reduce returns instead of lowering risk. Recognizing these common mistakes enables investors to build more effective portfolios.
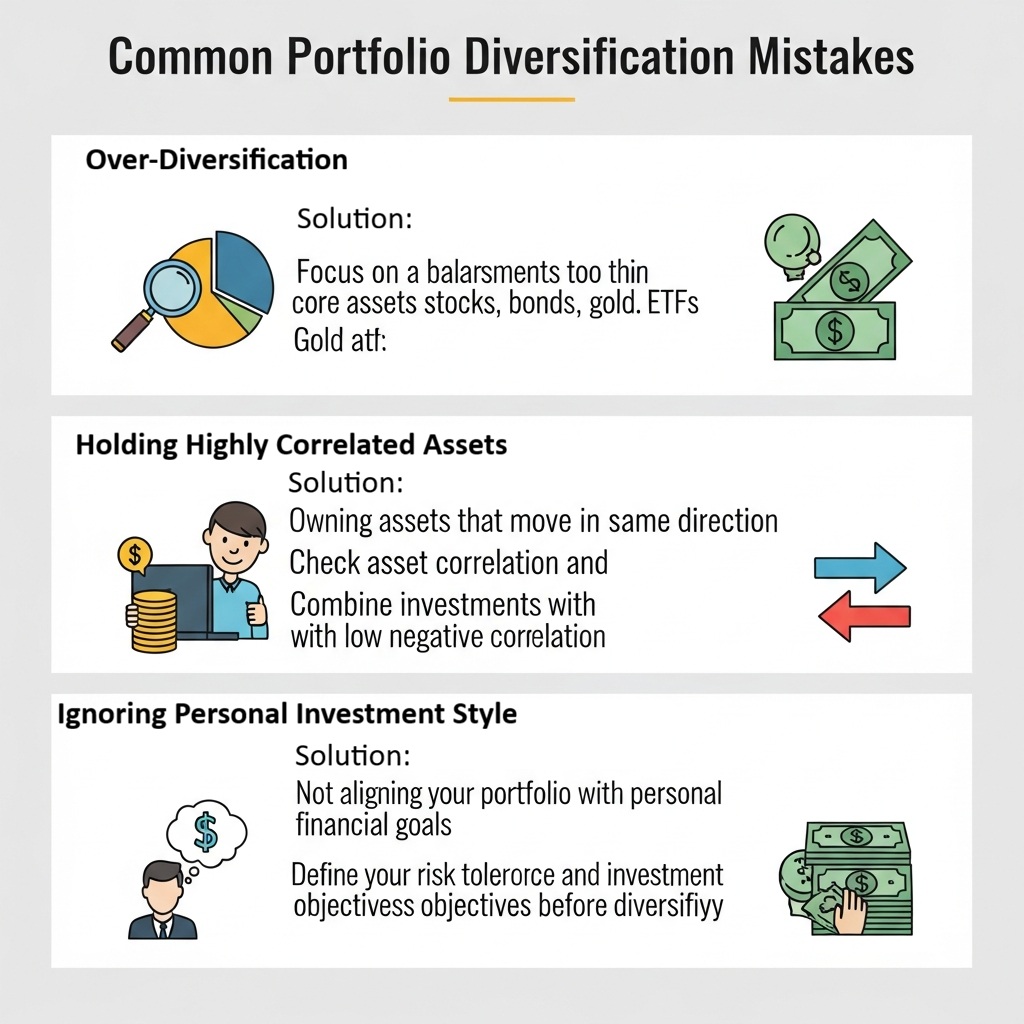
Over-Diversification
Holding too many assets makes a portfolio harder to manage and can dilute overall performance.
Solution:
Focus on a balanced mix of core assets, including stocks, bonds, gold, and ETFs.
Holding Highly Correlated Assets
When assets move in the same direction, such as stocks from the same industry, diversification loses its effect.
Solution:
Check asset correlation and combine investments with low or negative correlation.

Pro Tip:
Adding assets such as passive investments or blockchain-based investments can significantly reduce portfolio correlation and strengthen overall portfolio diversification.
Ignoring Personal Investment Style
Each investor’s investment style is shaped by their financial goals, time horizon, and risk tolerance. Ignoring these factors can lead to dissatisfaction, poor decision-making, and emotionally driven trades.
Solution:
Before implementing any portfolio diversification strategy, clearly define your risk tolerance and investment objectives, then design the portfolio accordingly.
Conclusion
Portfolio diversification is a core principle of smart investing. By spreading capital across different assets, industries, and even global markets, investors can significantly reduce overall risk. This approach increases resilience to market volatility and supports more stable long-term returns.
When combined with clear diversification strategies, portfolio analysis tools, and disciplined capital management, diversification helps investors build portfolios aligned with personal goals. It also improves protection against market shocks and unexpected volatility.































