Algorithmic Stablecoins are an innovative digital currency designed to tackle the biggest challenge in the crypto market: price volatility. This new class of assets seeks to maintain a stable value, not by relying on traditional dollar or gold reserves, but by utilizing automated algorithms and market mechanics to constantly adjust supply and demand.
While many view this decentralized model as a crucial step toward the evolution of the digital monetary system, others highlight its inherent risks and potential for instability. To truly understand how this unique type of stablecoin functions, why it has failed in the past, and whether it can genuinely shape the future of money, continue reading this comprehensive guide.

- Algorithmic Stablecoins are an attempt to create a form of digital money without physical reserves, maintaining stability purely through algorithms and economic logic.
- The future of these stablecoins depends on their ability to balance independence, transparency, and user trust.
- Integrating emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and hybrid models can pave the way for greater stability and long-term development.
- The long-term success of Algorithmic Stablecoins relies on regulatory acceptance, secure technical infrastructure, and effective risk management in the global market.
What Are Algorithmic Stablecoins and What Role Do They Play in the Crypto Economy?
To understand what an Algorithmic Stablecoin is, it can be defined as a type of digital currency that maintains its value close to one dollar without relying on fiat or crypto reserves. Instead of depending on real-world collateral like Tether (USDT) or USDC, this system uses algorithms and smart contracts to automatically adjust supply and demand, keeping the price stable.
In the crypto economy, this form of stablecoin plays a crucial role by increasing liquidity in the DeFi ecosystem, reducing reliance on traditional banking systems, and making global money transfers faster and easier. Among the more successful models, the FRAX project is considered one of the best examples of an Algorithmic Stablecoin as of 2025.

Although the main goal of an Algorithmic Stablecoin is to maintain its peg, some projects intentionally allow for slight price fluctuations to stimulate market activity and attract liquidity.
The Difference Between Algorithmic Stablecoins and Centralized Stablecoins Like Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC)
The key difference between Algorithmic Stablecoins and centralized stablecoins such as Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC) lies in their backing mechanism and the level of control over token supply. Centralized stablecoins are backed by fiat reserves, usually held in bank accounts, which gives them higher price stability but also exposes them to centralized oversight and potential transparency issues.
On the other hand, algorithmic models operate without fiat collateral. They rely on algorithms and automated supply adjustments to maintain price stability, offering greater independence from traditional financial systems. However, this autonomy comes with higher volatility and systemic risk.
If you are still wondering what a stablecoin is, it’s helpful to first understand the basic structure and purpose of these digital assets to better grasp how algorithmic models differ from their centralized counterparts.
Key Components in the Design and Function of Algorithmic Stablecoins
To understand how Algorithmic Stablecoins maintain their stability, it helps to look at the main parts that make up their system. These digital assets rely on three essential elements that work together to keep their value steady: supply adjustment algorithms, governance tokens, and oracles. Each of these components plays a specific role in helping the coin stay close to its target value of one dollar, even when the market becomes unstable.
Peg Mechanism and How Price Fluctuations Are Controlled
The peg mechanism is the foundation of every Algorithmic Stablecoin. Its goal is to keep the token’s value close to one dollar through an automated system that adjusts the supply. When the price rises above one dollar, the system creates more tokens to increase supply and bring the price back down. When the price falls below one dollar, tokens are removed from circulation to reduce supply and help the value recover. All of this happens automatically through smart contracts that react to real-time market data.
The Role of Governance Tokens in Balancing the System
Many Algorithmic Stablecoins use a second token called a governance token. Holders of this token can help decide how the system should operate, such as changing supply rules or adjusting key parameters. A well-known example was the LUNA project, which used this model to control supply and maintain price stability. Governance tokens are vital for the health of the system, but if investors lose confidence, it can lead to instability or even collapse.
The Importance of Oracles in Maintaining Stability
Oracles are systems that send real-world market data to the blockchain, such as the price of the U.S. dollar or Bitcoin. Accurate and timely information is crucial for an Algorithmic Stablecoin to function properly. If oracle data is wrong or delayed, the algorithm might make poor decisions, which can cause the coin to lose its peg. Many projects use reliable data providers like Chainlink to ensure that smart contracts receive precise and up-to-date information, helping the stablecoin remain steady even during volatile market conditions.
How Do Algorithmic Stablecoins Work?
To understand how an Algorithmic Stablecoin works, it is important to know that this type of digital currency operates without direct backing from fiat money or other crypto assets. Instead, it relies entirely on algorithms and smart contracts to maintain its value close to one dollar. The system automatically adjusts supply and demand to prevent major price fluctuations. This foundation has given rise to several models of Algorithmic Stablecoins, each using a different mechanism to keep prices stable.
Supply Adjustment Algorithms (Rebase Mechanism)
In this model, the total number of tokens in circulation changes according to market conditions. When the price rises above the target level, new tokens are created to increase supply and bring the price down. Conversely, if the price falls below one dollar, a portion of the tokens is removed from circulation to reduce supply and push the value back up. A well-known example of this model is the Ampleforth (AMPL) project, which uses automated supply adjustments to maintain stability.
Dual-Token Models and Seigniorage Shares
The Seigniorage model uses two types of tokens: one main stablecoin whose value is meant to stay fixed and a secondary token that absorbs market volatility. When the price rises above the peg, more of the main stablecoin is issued. When it falls below the peg, holders of the secondary token can burn their tokens to help reduce supply and restore balance. This mechanism has been used in projects like ESD to maintain price stability and protect the system’s equilibrium.
Fractional-Algorithmic Systems and Their Differences
Some Algorithmic Stablecoins use a hybrid approach that combines collateral and algorithmic controls. In this structure, part of the coin’s value is backed by crypto reserves, while the rest is managed through supply-adjusting algorithms. This mix helps reduce risk and increase price stability. The FRAX project is one of the most successful examples of this model, achieving a balance between financial security and decentralization.
The Role of Arbitrage Traders in Maintaining Price Stability
Arbitrage traders play an essential role in keeping Algorithmic Stablecoins stable. When the token’s price moves away from its one-dollar target, these traders step in to profit from the difference, helping the market rebalance. If the price goes above one dollar, they sell to bring it down. If it drops below one dollar, they buy to push it back up. This natural market mechanism helps restore equilibrium and keeps the stablecoin aligned with its peg.
Types of Algorithmic Stablecoins and How They Work
Algorithmic Stablecoins are designed in different ways to keep their price stable over time. Although each model uses a unique system, they all share one main goal, which is to maintain the value of the token close to one dollar. In general, there are four main categories of algorithmic stablecoins, and each of them uses a specific method to balance supply and demand in the market.
Rebasing Models and Automatic Supply Adjustment
In this model, the system automatically changes the number of tokens in circulation depending on market conditions. When the price of the token goes above one dollar, the system increases the total supply to bring the price down. When the price drops below one dollar, some tokens are removed from circulation to make the value rise again. The Ampleforth (AMPL) project is one of the first and best-known examples of this model and shows how supply changes can help maintain balance.
Seigniorage Models and Dual Token Systems
In the Seigniorage model, two tokens work together to stabilize the system. One token acts as the main stablecoin that should keep its price steady, while the second token is used to control volatility. When the price rises above the target level, new stablecoins are created. When the price falls, holders of the secondary token can burn it to reduce supply and help restore balance. Projects such as Basis Cash and Terra have used this structure to maintain stability in their ecosystems.
Fractional Models that Combine Collateral and Algorithms
Some Algorithmic Stablecoins use a combination of crypto collateral and algorithmic control to keep prices stable. In this approach, part of the token’s value is backed by assets such as USDC, and the rest is managed by algorithms that automatically adjust supply. The FRAX project is a strong example of this method and is often considered the best algorithmic stablecoin of 2025 because it successfully combines safety, flexibility, and independence.
Hybrid and Intelligent Stablecoin Models
A new generation of Algorithmic Stablecoins is emerging that combines several stabilization techniques with modern technologies like artificial intelligence. These intelligent models aim to make the system more stable and allow it to react faster to market changes. By using data-driven decision-making, they help ensure that the coin maintains its value even when the market becomes highly volatile.

There are also projects that use rotational mechanisms between different models, meaning they can switch from one stabilization method to another when a model becomes less effective.
Advantages and Use Cases of Algorithmic Stablecoins
Algorithmic Stablecoins offer several advantages thanks to their decentralized nature. Since they do not rely on fiat or crypto reserves, they can create sustainable liquidity in the market while using capital more efficiently. These coins play a vital role in the growth of the DeFi ecosystem, where they are used on platforms such as Uniswap for providing liquidity, lending, and executing smart trades. Their ability to operate without centralized control makes them an efficient and innovative option for decentralized financial markets.
Risks and Drawbacks of Algorithmic Stablecoins
Despite their innovative design, Algorithmic Stablecoins carry significant risks. The most critical one is the loss of the price peg, as seen in the collapse of UST, which resulted in more than 40 billion dollars in losses. These systems are also vulnerable to oracle attacks, where inaccurate price data can cause the algorithm to malfunction and destabilize the token. In extreme market conditions, a phenomenon known as the death spiral can occur, leading to a complete collapse in the value of the stablecoin.

Another major risk is cross-liquidity dependency. When an Algorithmic Stablecoin relies on a secondary or supporting token to maintain its balance, a failure in that secondary token can cause the entire system to collapse, even if the main algorithm itself remains functional.
Criteria for Choosing the Best Algorithmic Stablecoin
When selecting the best Algorithmic Stablecoin, several important criteria should be considered. These factors help determine which projects offer greater price stability, stronger liquidity, and wider user adoption. The most crucial aspects include peg stability, data transparency, trading volume, and the level of integration with leading DeFi platforms and exchanges.
Peg Stability and Historical Price Behavior
The primary factor is a project’s ability to maintain its peg to the dollar. For example, the FRAX project has successfully maintained price stability under most market conditions, while UST failed to do so during periods of market stress, resulting in a major price collapse.
Data Transparency, Auditing Reports, and Technical Credibility
Projects that publish regular audit reports and share their data transparently tend to be more trustworthy. The use of reliable oracles such as Chainlink and open-source code also indicates strong technical credibility and better community confidence.
Trading Volume, Liquidity Depth, and Peg Recovery Capability
Higher trading volume and deeper liquidity pools enable faster peg recovery when market volatility occurs. Reports show that in 2025, the average trading volume of Algorithmic Stablecoins increased by more than 30 percent, suggesting growing user confidence in these systems.
Adoption Across DeFi Platforms and Reputable Exchanges
The broader a stablecoin’s adoption across major platforms, the more stable and valuable it becomes. Integration into liquidity pools such as Curve or listings on trusted exchanges helps improve accessibility, encourages trading activity, and strengthens the coin’s position within the DeFi ecosystem.
How to Evaluate the Performance of an Algorithmic Stablecoin
To properly evaluate the performance of an Algorithmic Stablecoin, it is essential to analyze real blockchain data, also known as on-chain data. This information reveals whether the coin has been able to maintain its value close to one dollar over time. Tools such as Amberdata and DeFiLlama are commonly used to track stability, trading volume, and user behavior. Below are the key indicators used for a more detailed evaluation.
Key Peg Stability Metrics in Algorithmic Stablecoins
The most important factor is peg stability. If a token’s price fluctuates within less than one percent of its target, it indicates strong and consistent performance. An Algorithmic Stablecoin that can maintain its peg during volatile market conditions is considered more reliable and resilient.
On-Chain Data Analysis
On-chain data analysis helps us observe real market behavior. For example, during the 2020 market crash, the DAI stablecoin deviated only about two percent from its target price. Charts available on coinmarketcap clearly illustrate these fluctuations and how the system was able to recover and restore its peg over time.
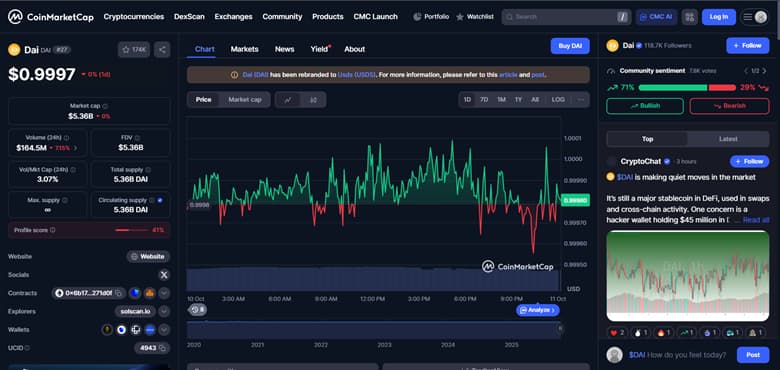
Liquidity Depth and Its Role in Peg Recovery
Liquidity depth refers to the amount of capital locked in the stablecoin’s liquidity pools. The higher this figure, the easier it becomes to restore the peg when the price falls. In general, projects that maintain a total value locked (TVL) greater than 30 percent of their market capitalization tend to demonstrate stronger stability and better market resilience.
Tools and Platforms for Monitoring Algorithmic Stablecoins
Platforms such as DeFiLlama, Nansen, and Amberdata provide valuable tools for tracking real-time changes in supply, transaction volumes, and liquidity levels. These analytics are especially useful for investors and analysts seeking to assess the ongoing performance of algorithmic stablecoins.
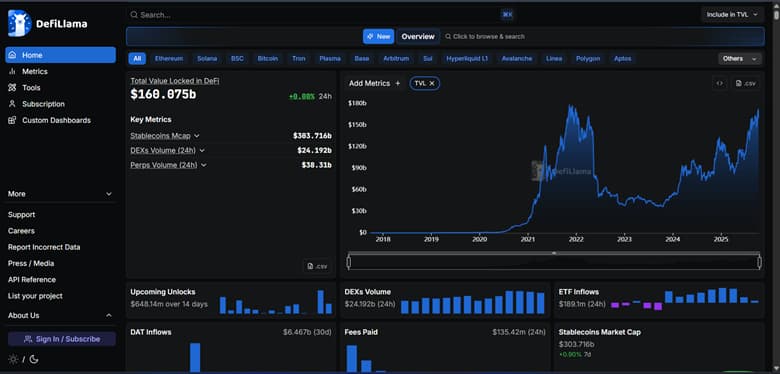
Historical Data Comparison and Peg Behavior in Crisis Conditions
Comparing historical data helps illustrate how different projects respond to market stress. For instance, while UST completely collapsed in 2022, FRAX managed to recover its peg by maintaining partial collateral and using adaptive algorithms. This demonstrates that not all models behave the same way under pressure, and studying these differences can guide better investment decisions.
Tokenomics Model in Algorithmic Stablecoins
One of the most important aspects in the design of an Algorithmic Stablecoin is its economic model, known as tokenomics. This model defines how tokens are created, burned, and distributed, as well as what incentives encourage users to participate in maintaining system stability. Essentially, tokenomics serves as the backbone of every project, showing how supply, demand, and price balance are managed to sustain the ecosystem.
Dual-Token Structure in Algorithmic Stablecoins
Many Algorithmic Stablecoins operate on a dual-token structure. One token functions as the main stablecoin, which is designed to maintain a value close to one dollar, while the secondary token is used to absorb volatility and help stabilize the system. This setup enables the protocol to adjust more effectively to market fluctuations and prevents the peg from being lost during periods of stress.
The Role of Mint and Burn Mechanisms in Supply Adjustment
The mint process refers to the creation of new tokens when the price exceeds the target value, helping to reduce the price by increasing supply. Conversely, the burn process removes tokens from circulation when the price falls below the peg, reducing supply and pushing the value upward. These mechanisms operate automatically through smart contracts, ensuring that supply dynamically adjusts to market conditions and the system remains in equilibrium.
The Role of Incentives in Maintaining System Balance
To encourage user participation and maintain long-term stability, many projects implement incentive mechanisms. These can include staking rewards, a share of transaction fees, or the distribution of new tokens. Such incentives motivate users to provide liquidity and actively support the ecosystem, ensuring that the Algorithmic Stablecoin remains both stable and sustainable over time.
Key Trading Strategies for Traders and Investors in Algorithmic Stablecoins
To operate effectively in the world of Algorithmic Stablecoins, traders and investors need to understand the balance between potential profit and risk. Two of the most important strategies in this area are arbitrage trading and risk management. When a token’s price moves away from its peg, it creates opportunities for profit based on price differences. At the same time, investors must be prepared for the risk of peg loss and take steps to protect their capital. Choosing the right stablecoin for participation in liquidity pools is also a key part of a successful strategy.
Using Peg Fluctuations for Arbitrage Trading
When the price of an Algorithmic Stablecoin falls below or rises above one dollar (known as depeg), traders can buy the token at a discount and wait for it to return to its peg to make a profit. These arbitrage opportunities not only provide earning potential but also help restore market balance, as traders’ actions push the price back toward the target level.
Best Risk Management Practices During Depeg Events
To manage risk effectively, diversification is one of the most reliable strategies. Investors should hold a mix of assets, including both Algorithmic Stablecoins and more stable tokens. Setting stop-loss levels, maintaining sufficient liquidity, and having a clear exit plan are essential tools for protecting funds when the peg weakens or market volatility increases.
Choosing the Right Algorithmic Stablecoin for Liquidity Pools
When providing liquidity, it is important to select a stablecoin with a strong history of peg recovery and price stability. Projects like FRAX are considered reliable options by many traders because they combine algorithmic control with partial collateralization, offering a balance between flexibility and resilience. This makes them a preferred choice for liquidity providers seeking stable yet profitable opportunities in decentralized finance.
Regulatory Landscape and Legal Challenges of Algorithmic Stablecoins
Despite their technical and economic innovation, Algorithmic Stablecoins still sit in a legal gray area in many jurisdictions. Regulators in the United States, the European Union, and elsewhere are working to establish clear frameworks for oversight and supervision.
In the United States, agencies such as the SEC and the Federal Reserve are still assessing whether stablecoins should be classified as digital currency, securities, or a new category of financial asset. This question is especially challenging for algorithmic models that operate without fiat collateral, since defining their legal nature is more complex.
In the European Union, the MiCAR framework provides a comprehensive regulatory regime for digital assets. However, algorithmic designs that lack real reserves may face stricter limitations, and in some cases issuance could be restricted altogether.
One of the biggest challenges for policymakers is transparency. Many countries expect issuers to publicly disclose details about their algorithms, source code, and peg-stabilization methods. This level of openness is essential for building user trust and preventing financial misconduct.
The Future of Algorithmic Stablecoins
Rapid advances in technology and the expansion of crypto markets make the outlook for Algorithmic Stablecoins dynamic and promising. By 2026, models that blend algorithmic control with collateral, incorporate artificial intelligence, and interact with central bank digital currencies are expected to become more stable and efficient. Below are the key trends to watch.
The Rise of Hybrid Models that Combine Collateral and Algorithms
Hybrid designs aim to capture the best of both worlds. Part of the token’s value is backed by real or crypto assets, while the rest is stabilized by algorithmic rules. This approach helps projects such as FRAX create steadier pricing and reduce the risk of sudden breakdowns.
Interaction and Competition with Central Bank Digital Currencies
As national digital currencies such as the e rupee expand, both cooperation and competition with Algorithmic Stablecoins are likely to increase. Stablecoins can complement CBDCs in areas like cross border payments and decentralized applications, although they may also face tighter regulatory requirements.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Improving Stability
Artificial intelligence can play a central role in forecasting and managing volatility. With access to large scale data, intelligent models can detect early signs of potential depeg events and adjust parameters before stress escalates. This capability can significantly strengthen user confidence and the long term stability of Algorithmic Stablecoins.
Conclusion
Despite the challenges, Algorithmic Stablecoins have shown the potential to become the foundation of a new generation of digital money. This form of currency operates without intermediaries and relies on trust in code and economic logic. The future of this field depends on technological advancement, greater transparency, and the development of clear regulatory frameworks that ensure stability and sustainable growth in the digital economy.































