If you’re searching for a safe broker in the Middle East, you’ll often come across the name DFSA. This independent regulator of the DIFC (Dubai International Financial Centre) enforces strict rules and transparent oversight to safeguard the credibility of Dubai’s financial market.
In this guide, you’ll learn what DFSA is, its key responsibilities, and how you can personally check the legitimacy of brokers regulated under this authority.

- DFSA regulation, with its strict oversight, client fund segregation, and transparent reporting, significantly reduces the risks of dealing with unregulated brokers.
- Alignment with global standards such as FATF and IOSCO has positioned DFSA alongside major regulators like the UK’s FCA and Australia’s ASIC.
- DFSA was one of the first authorities to introduce clear regulations for cryptocurrencies and stablecoins.
What Is DFSA Regulation and What Are Its Responsibilities?
According to the DFSA website, the Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA) is an independent regulatory authority operating within the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC). Essentially, it serves as the “financial watchdog” of this international free zone, with the main objective of creating a secure, transparent, and fair environment for investors and financial institutions.
Some of the key responsibilities and powers of the DFSA include:
- Supervising financial firms and brokerages: Ensuring their activities comply with international laws and standards.
- Combating money laundering and financial crimes: Enforcing strict KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) regulations.
- Enhancing market transparency: Requiring financial institutions to provide clear and accurate reporting to prevent fraud and misconduct.
- Financial markets tribunal: Holding financial court proceedings and imposing fines, restrictions, suspensions, and sanctions.
- Investor protection: Establishing a framework that safeguards the rights of traders and investors.
- Developing international standards: Aligning Dubai’s financial regulations with global rules to attract foreign investment.
History and Evolution of DFSA
The development of the DFSA can be summarized as follows:
- 2004: DFSA was established as part of Dubai’s financial free zone.
- 2017: DFSA launched the Innovation Testing Licence, a regulatory sandbox that allowed firms to test innovative products in a controlled environment.
- 2021: Introduced the Investment Token Regime, bringing digital assets under its regulatory framework.
- 2022: Released an enhanced version of this framework, extending oversight to areas such as cryptocurrency markets, anti–money laundering (AML), and counter-terrorist financing (CTF).
- By the end of 2023: The number of licensed firms reached 791, marking a 25% year-on-year growth.
- 2024: The regulator issued fines totaling $2.5 million.
- Early 2025: DFSA officially recognized the stablecoins USDC and EURC.
Table: History and Key Milestones of DFSA
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 2004 | Establishment of DFSA alongside the launch of the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC). |
| 2017 | Introduction of the Innovation Testing Licence (Sandbox) for testing innovative products and services in a controlled environment. |
| 2021 | 105 applications submitted for the sandbox; 51 firms accepted. |
| 2021 | Launch of the Investment Token Regime to regulate digital assets. |
| Nov 2022 | Introduction of the Crypto Token Regime, an advanced framework for cryptocurrency regulation. |
| Jun 2024 | Amendments to the Crypto Token Regime, including: permission for eligible domestic funds to invest up to 10% in unrecognized crypto assets; reduction of token recognition fees from $10,000 to $5,000; and new criteria for stablecoins. |
| 2023 | Licensing and registration of 117 new firms by the DFSA. |
| 2024 | Issuance of $2.5 million in fines. |
| Early 2025 | Official recognition of USDC and EURC stablecoins. |
| May 2025 | Appointment of Mark Steward, former UK FCA director, as the new CEO of DFSA. |
Which Companies and Financial Institutions Need a DFSA License?
Any company that wants to provide financial services within the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC) is required to obtain a DFSA license. This license is not only a legal obligation but also plays a crucial role in building trust among investors and clients. By setting clear frameworks and strict standards, DFSA ensures that all activities are conducted professionally, transparently, and in line with international regulations.
The main categories of institutions and companies that must be licensed by DFSA include:
- Brokerages and trading firms: All Forex, CFD, and equity brokers operating within the DIFC.
- Banks and credit institutions: Both local and international banks providing banking and credit services under DFSA supervision.
- Asset management firms and investment funds: Entities managing investment portfolios or establishing investment funds.
- Insurance and reinsurance companies: Firms offering various types of insurance services within the DIFC.
- FinTech companies and innovative service providers: Especially those involved in cryptocurrencies, digital payments, blockchain, and tokenization.
- Financial and investment advisors: Companies offering financial advisory, wealth management, or investment guidance.
- Exchanges and payment service providers: Including payment platforms and international money transfer services.
Complete Process of Applying for and Obtaining a DFSA Regulatory License
Obtaining a license from the DFSA is one of the most important prerequisites for starting legal operations within the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC). This multi-stage process is designed to ensure that only firms capable of delivering transparent, professional services in line with international standards can enter the market.
The general steps for applying for and obtaining a DFSA license are as follows:
- Submission of the Initial Application
The applicant must first submit a preliminary application along with a description of the intended activities to the DFSA. This initial application can be completed and filed through the DFSA’s official website, where the applicant outlines the nature of the business, the type of financial services offered, and the operational framework.
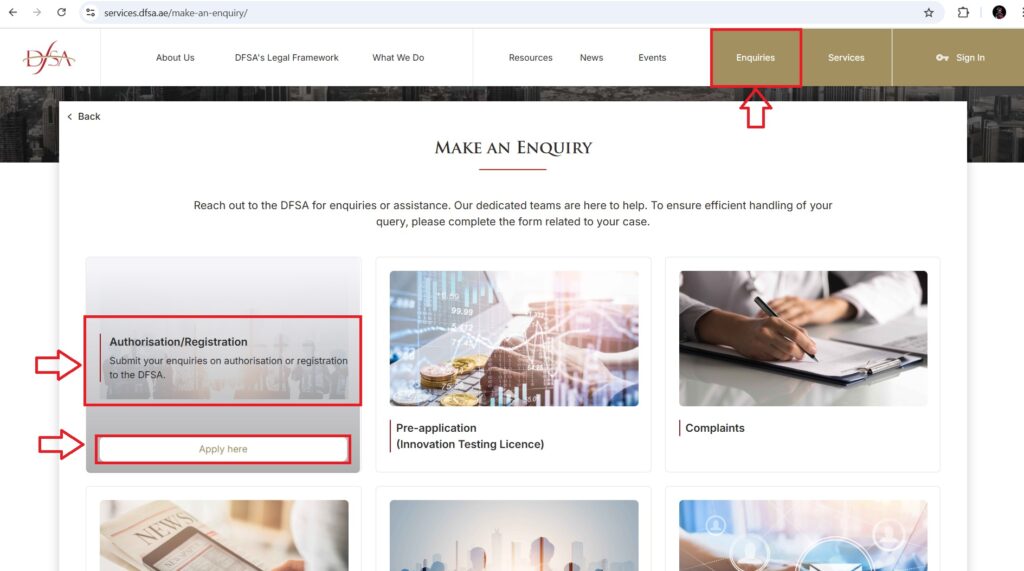
- Preliminary Meeting with DFSA
After the initial review, a meeting is held between the applicant company and DFSA experts to discuss legal requirements, required documentation, and the alignment of the proposed activities with the regulatory framework. - Submission of the Formal Application
At this stage, the applicant must complete the official DFSA regulatory forms and provide documents such as a business plan, organizational structure, financial reports, risk management policies, and internal procedures including AML/KYC. - Fit and Proper Assessment of Directors and Shareholders
DFSA evaluates key individuals of the company (directors, major shareholders, and risk managers) in terms of professional competence, work history, and financial capability. - Review of Control and Operational Frameworks
The applicant must demonstrate the presence of strong control systems, anti–money laundering (AML) procedures, financial transparency, and internal compliance structures. - Payment of Fees
Application and licensing fees vary depending on the type of financial activity and must be paid to the DFSA. - License Issuance (Authorisation)
Upon final approval, DFSA issues the license. From this stage onward, the company is legally authorized to provide financial services within the DIFC. - Ongoing Supervision After Licensing
Receiving the license is not the end of the process. Firms regulated by the DFSA are required to submit regular financial and operational reports and comply continuously with AML laws, transparency standards, and investor protection requirements.
Costs, Documentation, and Legal Requirements for Obtaining a DFSA License
Securing a license from the DFSA is a serious, multi-step process that not only involves a thorough assessment of the company and its management but also requires the payment of fees and submission of specific legal documents. This ensures that only transparent, sound, and professional firms are allowed to operate within the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC).
Licensing Costs
- The fees for obtaining a license vary depending on the type of financial activity (e.g., brokerage, banking, asset management, financial advisory, etc.).
- Costs typically include an application fee, document review fees, and an annual license maintenance fee.
- For certain activities, such as digital asset services, separate charges are applied. For example, in recent years, the token recognition fee was reduced from $10,000 to $5,000.

To learn more about the costs of obtaining and renewing regulatory licenses with the DFSA, click here.
Required Documentation
Firms must submit a comprehensive set of documents and information to the DFSA, including:
- A detailed business plan outlining objectives, revenue model, and financial projections.
- The organizational and shareholding structure, with full details of major shareholders and key executives.
- Internal policies and procedures for risk management, internal controls, and compliance with AML/KYC regulations.
- Financial records and audited reports to demonstrate the company’s financial stability.
- Identification documents and professional backgrounds of directors and shareholders for fit and proper assessment.
Legal Requirements
- Full compliance with the DIFC Regulatory Law of 2004, which forms the basis of DFSA’s powers and responsibilities.
- Adherence to international standards, including FATF regulations on anti–money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorist financing (CTF).
- Submission of periodic financial and operational reports to the DFSA to demonstrate transparency and sound practices.
- Having dedicated in-house Compliance and Risk Management teams within the company’s structure.
Scope of DFSA’s Regulatory Authority in Dubai
The DFSA’s regulatory scope is broad, covering banks, brokerages, investment firms, funds, fintech companies, and even the digital assets market.
In addition to licensing, the DFSA is responsible for monitoring compliance with anti–money laundering (AML) laws, counter-terrorist financing (CFT) measures, investor protection, and the enforcement of international standards such as IOSCO and FATF.
Regulations for Banks and Credit Institutions under DFSA Supervision
Banks and credit institutions operating within the DIFC must be regulated by the DFSA. The rules for banks are designed primarily to protect depositor confidence and ensure financial system stability.
Key requirements for banks and credit institutions under DFSA include:
- Maintaining adequate initial capital and meeting capital adequacy standards.
- Adhering to risk management and liquidity policies.
- Complying with KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML rules to prevent money laundering.
- Providing transparent, audited financial reports to the DFSA.
- Having a qualified board of directors and senior management, whose fitness and propriety are approved by the DFSA.
Legal Requirements and Standards for Brokerages and Brokers Regulated by DFSA
Brokerages and brokers are among the key entities operating under DFSA’s strict regulatory framework. The main purpose of these regulations is to protect traders and retail investors.
Key Requirements for Brokers under DFSA Regulation:
- Segregation of client funds from the company’s operational capital.
- Transparent order execution systems without manipulation or conflicts of interest.
- Full compliance with AML (Anti–Money Laundering) and KYC (Know Your Customer) requirements.
- Providing comprehensive risk disclosure to clients before they start trading.
- Maintaining compliance teams and submitting regular reports to the DFSA.
These requirements ensure that DFSA-regulated brokers hold strong international credibility, giving traders greater confidence and peace of mind when working with them.
How DFSA Oversees Investment Activities and Dubai’s Financial Markets
The DFSA not only supervises banks and brokers but also oversees capital markets and investment activities. It sets frameworks for asset management, investment funds, financial advisory services, and even initial public offerings (IPOs) within the DIFC.
DFSA’s Oversight Methods in Capital Markets Include:
- Reviewing and approving securities offering documents.
- Assessing the qualifications of asset management firms and investment advisors.
- Requiring investment funds to provide periodic and transparent reports.
- Monitoring suspicious trades and combating market manipulation or insider trading.
- Developing modern regulatory frameworks for digital assets and tokens.
How DFSA Differs from Other Regulators
To better understand the position of DFSA, it’s important to compare it with other major global regulators such as the UK’s FCA, Cyprus’s CySEC, and Australia’s ASIC.
DFSA vs. UK FCA
- Regulatory Scope: The FCA is a national regulator overseeing the entire UK financial market, whereas DFSA’s authority is limited to activities within the DIFC.
- Strictness: Both authorities take AML (Anti–Money Laundering) and KYC (Know Your Customer) requirements very seriously, but the FCA has a longer track record of financial transparency and enforcement.
- International Reputation: The FCA is recognized worldwide as one of the toughest regulators. DFSA, however, has significantly strengthened its standing in recent years by adopting modern frameworks such as the Crypto Token Regime, bringing it closer to top-tier global regulators.
DFSA vs. CySEC Cyprus in the Brokerage Sector
- Scope of Activity: CySEC primarily regulates Forex and CFD brokers within the European Union, while DFSA’s scope is broader, covering not only brokers but also banks, insurers, investment funds, and even fintech firms.
- Client Protection: CySEC enforces requirements such as segregation of client funds and mandatory participation in the Investor Compensation Fund (ICF). DFSA also mandates client fund segregation but places stronger emphasis on anti–money laundering measures and transparent reporting.
- Reputation: CySEC is widely recognized among retail brokers, whereas DFSA holds greater credibility with institutional investors and international banks.
DFSA vs. Australia’s ASIC
- Geographic Scope: ASIC is Australia’s national regulator, overseeing both domestic and international markets. DFSA, by contrast, operates exclusively within the DIFC but aligns its rules with global standards.
- Regulatory Approach: ASIC is known for its strict stance on broker advertising and restrictions on trading leverage. Similarly, DFSA has introduced limitations in recent years to protect traders and reduce risk exposure.
- Focus: ASIC places strong emphasis on online brokers and CFDs, whereas DFSA covers a much broader range of financial entities and activities.
DFSA’s Standing and Credibility Compared to Leading Global Regulators
Initially, the DFSA was recognized mainly as a regional regulator in Dubai. Today, however, through the introduction of advanced frameworks for digital assets, alignment with international bodies such as FATF and IOSCO, and its oversight of international banks, brokers, insurers, and funds, it has positioned itself alongside top-tier regulators like the FCA (UK), ASIC (Australia), and MAS (Singapore).
In effect, the DFSA serves as a bridge between Middle Eastern financial markets and strict global standards—an achievement that has boosted foreign investor confidence and strengthened Dubai’s role as a major international financial hub.
Advantages and Importance of DFSA Regulation for Traders and Investors
The key benefits of DFSA regulation for traders and investors include:- Client Fund Protection: Brokers and financial institutions under DFSA supervision are required to segregate client funds from company assets. This reduces the risk of misuse or investor losses in the event of bankruptcy.
- Financial Transparency: The DFSA obliges supervised firms to provide transparent, audited financial reports—minimizing the chances of misconduct or financial manipulation.
- Broker Conduct Oversight: Order execution, pricing, and broker advertising are closely monitored by the DFSA. This reduces the likelihood of price manipulation or conflicts of interest between brokers and clients.
- Anti–Money Laundering (AML) and Financial Crime Prevention: With strict AML and KYC requirements, investor security is reinforced, eliminating risks associated with suspicious or unregulated environments.
- International Credibility: A broker or institution regulated by the DFSA enjoys higher global recognition, making it easier for foreign investors to trust and engage with them.
- Coverage of Emerging Financial Sectors: Unlike many regulators, the DFSA has introduced modern rules for fintech, blockchain, and digital assets—creating new opportunities for traders and investors in the crypto space.
Why Does DFSA Regulation Matter?
DFSA essentially acts as a seal of trust. When a broker or financial institution operates under its supervision, traders and investors can be confident that:- Their funds are safeguarded under the oversight of a reputable regulator.
- In case of disputes or issues, clear legal remedies and transparent procedures are available.
- Financial institutions operate in line with international standards.
How to Verify a Broker’s DFSA License
One of the biggest concerns for traders when selecting a broker is the authenticity of its regulatory license. Even if a broker claims DFSA oversight, it’s always wise to verify this yourself to ensure your capital is protected in a secure environment.Steps to Check a Broker’s DFSA Authorization
Verify on the official DFSA website Go to the Public Register section and search under Firms for the broker’s name.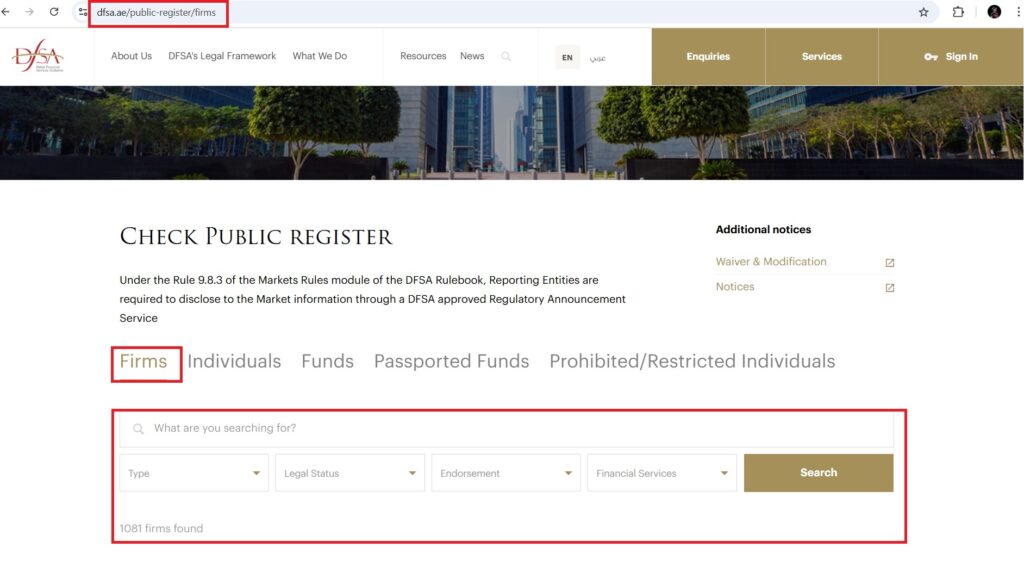
If Valid, the Following Information Will Be Displayed:
- License number;
- Date of issuance;
- Scope of activity;
- Current status (Active / Suspended).
Checking the License Number
Every DFSA-regulated broker is assigned a unique license number. This number must exactly match the one published on the broker’s official website.
Reviewing the Scope of Services
Some brokers are authorized only to provide advisory services, while others may have permissions for execution services or asset management. Ensure the broker’s scope of activity aligns with your trading or investment needs.
Verifying Financial Transparency
DFSA-regulated brokers are required to publish audited and transparent financial reports. Reviewing these reports can be a good indicator of the company’s financial health.
Direct Contact with DFSA
If you have any doubts, you can verify a broker’s legal status directly by reaching out via email or using the official contact forms on the DFSA website.
Conclusion
DFSA is not just a name on paper—it’s a practical framework designed to protect your capital. By understanding the regulator’s role and authority, knowing the licensing process, and performing due diligence through the DFSA Public Register, you can choose a broker that meets global standards while safeguarding your peace of mind. Taking the extra step of cross-checking a broker’s documents with the DFSA registry can turn a simple verification into a lasting competitive advantage for your trading journey.































