The S&P 500 ETF (SPY) is the most liquid trading instrument in the world. Traders often use SPY options to capture daily moves with small capital outlays. However, without a formal process, these fast-moving contracts can quickly deplete a retail account.
Effective trading requires more than just a directional bias or a gut feeling. You must understand the mathematical risks of time decay and the mechanics of liquidity. This guide provides a structured routine to manage risk while navigating the SPY market.

- Most SPY options feature penny-wide spreads, which lowers the total cost of entering a trade.
- The ETF structure allows for physical delivery of shares upon the contract's expiration.
- Market makers provide the bulk of liquidity, ensuring trades can be executed at almost any time.
- High liquidity means your stop-loss orders are less likely to suffer from significant price slippage.
What Does Trading SPY Options Mean?
According to Trade Station, Trade SPY options are contracts based on the SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust. They allow you to speculate on the top 500 US companies simultaneously. When you trade SPY options, you buy the right to trade the ETF at a set price. This must happen before a specific expiration date.
Core Components of Trade SPY Options
- Strike Price: The price at which you buy or sell the ETF.
- Premium: The cost you pay to own the option contract.
- Expiration: The date the contract becomes invalid or settles.
Traders use these for leverage, hedging, or generating daily income through volatility. They are highly liquid and trade almost every business day.
Market Access and Trading Sessions
Many traders confuse stock extended hours with options trading sessions. This confusion leads to poor planning and unexpected forced exits. You must understand the specific rules for the SPY instrument.
Standard Hours vs Extended Stock Sessions
Stocks often trade in pre-market and after-hours sessions. However, most ETF options do not trade during these extended times. Trading without institutional volume during these hours increases your risk.
The 15-Minute ETF Trading Extension
The OCC states most ETF options trade from 09:30 to 16:00 ET. For broad-based ETFs like SPY, trading runs until 16:15 ET. This extra window allows for final adjustments after the cash close.
Restrictions on Pre-Market and After-Hours Access
Most ETF options remain closed outside of the regular US session. If you need overnight access, you should consider trading index futures. Standard SPY options will not allow you to exit positions at midnight.

Key Point:
While some products trade until 16:15 ET, expiring weeklies may stop early. Always confirm the exact cut-off time with your specific broker.
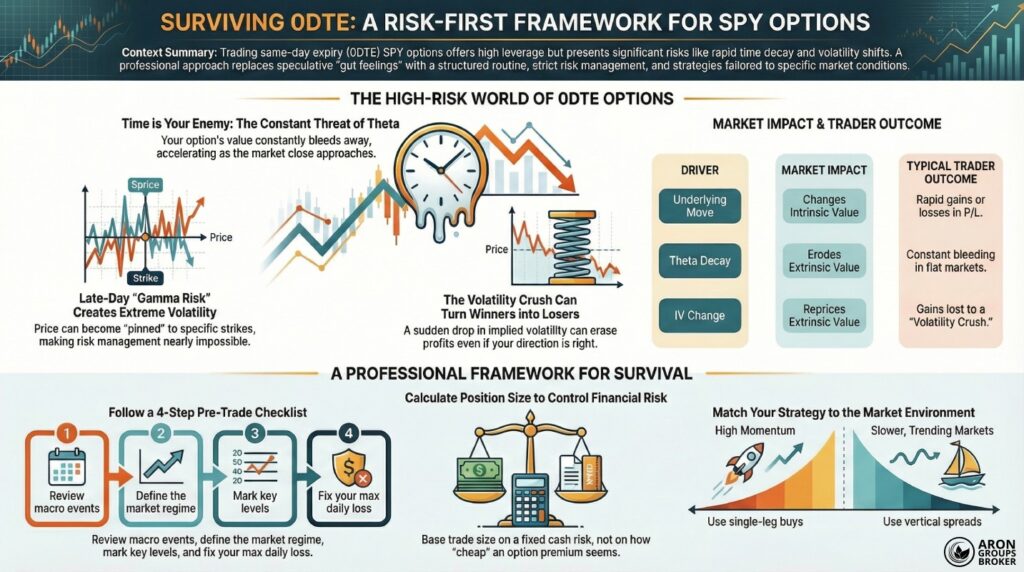
Risks of 0DTE SPY Options
0DTE SPY options expire on the same trading day, so pricing reacts sharply to small SPY moves. Because time value decays quickly, a flat market can still produce losses for option buyers.

Key Point:
0DTE options are all-or-nothing instruments. Most retail traders use them for speculation, but they require precise timing to succeed.
The Mechanics of 0DTE Contracts
A 0DTE option possesses very little remaining time value. This causes the price to react sharply to changes in the underlying ETF. Volatility shifts also have a more immediate impact on these premiums.
Bid-ask spreads are a critical factor for frequent day traders. Wide spreads can represent a large percentage of the total trade cost. Friction from these costs can significantly reduce your net returns.
Managing Theta: Why Stagnant Prices Lead to Losses
Theta represents the time decay of an options contract. If the SPY price remains flat, a long option loses value. The rate of this decay is not constant throughout the day.
Decay often accelerates as the market approaches the closing bell. This makes late-session 0DTE trading structurally more difficult for buyers. You must be right about the direction and the speed of the move.
Core Risk Variables: Delta, Gamma, Vega, and Implied Volatility
- Delta shows how much the option price moves for each 1% move in SPY.
- Gamma shows how quickly delta changes, which can spike near expiry for at-the-money options.
- Vega measures sensitivity to implied volatility (IV). If IV falls, premiums can drop even when the price moves in your favour.
- IV reflects the market’s expected future movement, so a high IV usually means higher premiums. After major news, IV often compresses quickly, erasing gains from the underlying move. Check IV before entering 0DTE trades, because volatility pricing can dominate short-term outcomes.
Table: Primary Drivers of 0DTE Profit and Loss
| Driver | Market Impact | Typical Trader Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Underlying Move | Changes Intrinsic Value | Rapid gains or losses in P/L. |
| Theta Decay | Erodes Extrinsic Value | Constant bleeding in flat markets. |
| IV Change | Reprices Extrinsic Value | Gains lost to Volatility Crush. |
| Gamma | Alters Delta Stability | Risk spikes during the final hour. |

More Info:
Gamma risk peaks near expiration. This can lead to "pinning," where the price settles exactly at a strike.
Q: What happens if you hold an in-the-money SPY option through the close?
A: SPY options feature physical settlement. You will be assigned or delivered 100 shares of the ETF per contract held.
Operational Routine for Daily Trading
A structured routine turns speculative activity into a testable business model. It limits impulsive decisions and ensures consistency across different market regimes. This framework is designed for active intraday execution rather than long-term investment.
You must be willing to stay on the sidelines if conditions are poor. A professional trader prioritises setup quality over trade frequency. Establishing these habits creates a safety net for your trading capital.
A Structured Four-Step Pre-Trade Checklist
- Macro Review: Confirm major risk events and scheduled economic releases.
- Market Regime: Define if the market is trending, range-bound, or event-driven.
- Reference Levels: Mark high-volume areas and previous day extremes.
- Risk Parameters: Fix your maximum daily loss before opening a position.
Identifying Value Areas Using Volume Profile
Volume Profile highlights the price levels where the most trading activity occurred. It allows you to separate fair value from price extremes and emotional spikes. The Value Area represents the zone where 70% of the day’s volume was transacted.
Use these zones to identify where the market is likely to stall or reverse. Trading at the edges of the Value Area provides clear invalidation points. Avoid entering trades during a high-volume node to reduce noise.
Selecting Strike Prices and Entry Points
Your chosen strike price is not the same as your technical entry price. The entry price is the premium you pay and the level you must defend. Choose strikes based on your expected holding time and directional conviction.
For fast scalps, higher Delta options offer better sensitivity to price moves. If your thesis requires more time, look for strikes closer to the money. Ensure the bid-ask spread is tight enough to allow for a cost-effective exit.
Execution Rules for Stop Losses and Targets
Define your stop loss based on price structure rather than emotional discomfort. If your technical invalidation level breaks, you must exit the trade immediately. Professional traders never hope for a reversal when a level is lost.
Plan your profit targets in areas where the market is likely to find resistance. Use partial exits to lock in gains as the trade moves in your favour. This strategy reduces your remaining risk while leaving room for further upside.
Calculating Position Size and Financial Leverage
Position size must be linked to a fixed cash risk for every single trade. If the technical stop is wide, your contract size must be reduced accordingly. Never risk more than a small percentage of your total equity on one setup.
A simple sizing formula is:
Cash risk ÷ Stop cost per contract = Number of Contracts
This ensures that one bad trade cannot significantly damage your overall account. Respecting leverage is the only way to survive high-volatility sessions.

Key Insight:
FINRA warns that the high leverage in day trading can lead to rapid losses. Always prioritise risk management over potential returns.
Q: What specific metrics should you record in a SPY options journal?
A: You should log the entry Delta, Implied Volatility (IV) at entry, and the bid-ask spread width. Recording slippage, the difference between your limit price and the actual fill, helps you track real execution costs.
Strategic Frameworks for Short-Term Contracts
This section outlines practical short-term SPY options setups, with clear conditions and exits designed for fast-moving intraday contracts.
Conditions for Single-Leg Option Trades
Single-leg buys are most effective when you anticipate immediate, fast price movement. These positions are extremely fragile during slow, range-bound market sessions. The lack of momentum allows time decay to erode your premium rapidly.
You must implement strict time-based stops for every single-leg trade. If the expected move does not occur quickly, you should exit the position. Do not wait for a price stop if the clock has already killed the setup.
Mitigating Decay with Vertical Spreads
Vertical spreads involve buying one option and selling another at a different strike. This combination reduces the total premium paid and softens the impact of Theta. It creates a more stable P/L curve during periods of market consolidation.
The primary trade-off is that vertical spreads cap your maximum potential profit. However, this limitation often improves discipline by providing a clear target. It is an excellent tool for traders who struggle with late-session volatility.
A Standardised Session Execution Plan
Select one specific trading window where you demonstrate the most consistency. Many successful traders focus on the market open or the final ninety minutes. Concentrating your energy prevents overtrading during low-probability mid-day hours.
Maintain a fixed maximum number of trades for every daily session. Two high-quality attempts usually produce better results than ten reactive ones. Quality of execution is far more important than the quantity of trades.
| Strategy Type | Best Environment | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Single-Leg Buy | High Momentum / Breakouts | Unlimited Profit Potential |
| Vertical Spread | Steady Trends / Slow Moves | Reduced Cost and Decay |
| Time-Based Exit | All Environments | Preserves Remaining Capital |

More Info:
Many brokers enforce auto-liquidation rules for same-day expiries. They may close your position early if you lack the capital to exercise.
Q: How does “Gamma Hedging” by market makers impact SPY price action?
A: Market makers must buy or sell SPY to stay neutral as prices move. Large Gamma levels can act as magnets, pinning the price to specific strikes.
Swing Trading Strategies with Weekly Expiries
Swing trading means holding SPY option positions for several days to capture a wider move. Weekly expiries suit traders who prefer planned entries over constant intraday decisions.
Benefits of Extended Time Horizons
Weekly options improve planning because you can build a trade around higher-timeframe levels. You can define entry, invalidation, and target zones before the session starts.
They also support structured trade management. You can scale in, scale out, and adjust only at pre-set review times. This approach reduces decision fatigue and the need for random mid-session changes. It is often easier to execute consistently alongside a full-time schedule.
Optimal Timeframes for Multi-Day Positions
Plan multi-day trades using daily and weekly charts first. Those levels usually carry more weight than short intraday patterns. Match your stop distance to your intended holding time. A swing trade needs room to breathe, so scalping stops usually fail.
Use intraday charts only to refine entries near key levels. Do not let short-term noise override your higher-timeframe thesis.
Navigating Overnight Gaps and Event Risk
Treat overnight gaps as a separate risk, not a surprise. Assume the price can open beyond your stop after major news. Control this risk with position size first. A smaller size is the simplest protection against gap losses.
Use defined-risk structures when you must hold through events. Vertical spreads cap worst-case loss by design. Keep an event calendar and set rules for holding through releases. If you cannot quantify the risk, reduce exposure or stay flat.
| Feature | Day Trading (0DTE) | Swing Trading (Weekly) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Risk | Immediate Theta Decay | Overnight Price Gaps |
| Chart Focus | 1-min / 5-min Intervals | Daily / Weekly Levels |
| Decision Speed | High / Rapid Execution | Moderate / Planned Entries |
| Leverage | Extremely High | Moderate to High |

Did You Know?
Equity and ETF options are American-style, meaning assignment can happen at any time before expiry. This differs from European-style index options.
Q: How do dividends impact the pricing of SPY call options?
A: When SPY goes ex-dividend, the share price typically drops by the dividend amount. This can increase the risk of early assignment for deep-in-the-money calls.
Regulatory Constraints: The Pattern Day Trader Rule
The Pattern Day Trader (PDT) rule limits frequent day trading in US margin accounts. FINRA requires pattern day traders to maintain at least $25,000 in account equity. If equity falls below that level, your ability to day trade can be restricted.
Definition of a Day Trade under FINRA Rules
A day trade is buying and selling the same security on the same day. A “pattern day trader” is typically triggered by four or more day trades in five business days. Your broker may apply additional controls, so always confirm their exact threshold.
Consequences of Account Restrictions
Restrictions can block new intraday entries, even when your setup is valid. That often leads to fewer trades, slower adjustments, and missed exits when conditions change.
A practical risk is being pushed into holding trades longer than intended. If your trading plan depends on quick exits, forced holding can break your risk model.
Portfolio Management for Smaller Accounts
Design a plan that works with your trade frequency limits, not against them. Fewer, higher-conviction setups usually outperform reactive overtrading. Use a strict daily loss limit and a maximum trades-per-day rule. Track your day-trade count and stop early if you are close to a trigger.
Shift some activity to lower-frequency structures when needed. Weekly expiries and defined-risk spreads can reduce turnover and decision pressure. Avoid “workarounds” that ignore broker rules or settlement realities. If PDT applies to you, align your strategy with it, or your strategy will fail operationally.
| Feature | Margin Account (<$25k) | Margin Account (>$25k) |
|---|---|---|
| Day Trade Limit | 3 trades per 5 business days | Unlimited day trades |
| Equity Requirement | No specific minimum | $25,000 minimum equity |
| Buying Power | Standard 2x for stocks | 4x day trading buying power |
| Regulation Type | FINRA PDT Rule | FINRA PDT Rule |
Q: Do options trades in a cash account settle as quickly as stock trades?
A: No, options trades usually settle on a T+1 basis, meaning the funds are available the next business day. This differs from the T+2 settlement cycle traditionally used for most stocks.
Comparative Analysis: Options and CFDs
Comparing options and CFDs is not a debate over which is better. It is a structural choice based on the specific risks you are willing to pay for. Options traders pay for time and volatility, while CFD traders pay for financing and margin.
CFDs remove the complexity of Theta decay but introduce ongoing interest costs for overnight holds. Options include a time-decay cost that works against you each hour you hold the contract. Your choice should align with your specific trading timeframe and risk tolerance.
Structural Differences in Directional Trading
With SPY options, you must be right about both the direction and the timing. With CFDs, your primary concern is direction, but leverage can still lead to rapid losses. The pricing of a CFD is transparent and directly tracks the underlying ETF price.
PDT rules are a major constraint for US margin traders using standard options. However, UK-based CFD providers typically operate under FCA protections rather than US PDT rules. This often allows UK retail traders more flexibility in their intraday execution frequency.
Margin Requirements and Financing Costs
The FCA mandates strict leverage limits for retail CFD accounts to prevent excessive risk. Most major equity CFDs are capped at 5:1 leverage for retail investors in the UK. These rules also include negative balance protection to ensure you cannot lose more than your balance.
If you hold a CFD position overnight, you will be charged a financing or swap fee. Options do not have interest fees, but their value erodes daily due to the Theta Greek. Ensure you calculate these hidden costs when planning a multi-day directional trade.
Selecting the Appropriate Instrument for Your Goals
Choose your instrument based on your specific market edge and capital constraints. If your trading strategy relies on high-speed directional breaks, options provide non-linear, explosive leverage. If you prefer a slower approach with simpler pricing, CFDs may be more suitable.
Always respect the impact of financial leverage on your total account equity. Regardless of the instrument, over-leveraging is the most common cause of retail trading failure. Consistency is found in managing risk, not in picking the perfect derivative.
Table: Options vs CFDs for Short-Term Traders
| Feature | SPY Options | CFDs (UK Context) |
|---|---|---|
| Time Decay | Yes (Theta) | No (Pure Price Track) |
| Key Risks | Greeks and Volatility | Margin and Financing |
| Protections | Exchange Clearing | FCA Negative Balance Protection |
| Market Style | Centralised Exchange | Over-the-Counter (Broker) |
Preventing Common Execution Errors
Most financial losses stem from execution errors rather than a lack of indicators. Improving your execution habits often yields better results than adding complex technical filters.
Avoiding Over-Analysis of Minor Price Action
Do not treat every minor candle wick as a meaningful piece of market information. Wicks frequently reflect intraday microstructure rather than a genuine change in trend. Using too many signals can lead to “analysis paralysis” and missed opportunities.
Simplify your chart by focusing on high-probability filters and major volume levels. Your objective is to make fewer decisions with higher levels of conviction. Reduce the noise to see the true direction of institutional order flow.
Monitoring Gamma and Expiry Risks
Gamma risk accelerates significantly as a contract approaches its expiration time. This can cause a stable position to become highly volatile within a few minutes. If you are trading late-session 0DTE options, you must reduce your position size.
Tighten your decision window to avoid being trapped in a “pinning” scenario. Gamma sensitivity makes it difficult to manage risk when the price is near the strike. Professional traders often exit 0DTE positions well before the final hour of trading.
Why Cheap Premiums Can Still Be High Risk?
A “cheap” option premium does not automatically represent a low-risk trading opportunity. Low contract prices often hide a mathematically high probability of a total loss. Focus on your expected loss in pounds rather than on the contract’s nominal price.
Size your positions based on your total risk tolerance, not on what you can afford. Buying “lottery ticket” options is a quick way to deplete a small trading account. Always prioritise high-probability strikes over cheap, out-of-the-money contracts.
Maintaining Discipline Within Trading Windows
Identify and stick to specific trading windows where market liquidity is most consistent. Tight spreads and high volume are essential components of your technical edge. Avoid executing trades when you are tired, distracted, or emotionally compromised.
Your trading process must be robust enough to survive your own bad moods. Consistency is a result of following a plan when you least feel like doing so. Market conditions vary throughout the day; trade only when your edge is present.
Clarifying Settlement and After-Hours Limits
Do not rely on being able to manage SPY options after the session ends. Check your broker’s cut-off times for opening and closing, especially for same-day expiry. If you ignore these limits, you can be forced into unwanted exercise or assignment risk.

Did You Know?
While many ETF options trade until 16:15 ET, certain expiring weekly contracts may stop trading exactly at 16:00 ET. Always check your contract's specific terms and conditions.
Conclusion
The most effective way to trade SPY options is rarely found in a secret strategy. It is a disciplined combination of strict risk limits, timing, and honest performance review. If you cannot explain your entry with logic, you are gambling on adrenaline.
Treat 0DTE contracts as a specialist tool rather than your default trading instrument. If you require less time pressure, shifting to weekly expiries may better suit your style. Protect your capital first, and the profits will eventually follow.